Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Distinguish between intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductor. (Give any two points).
उत्तर
| Intrinsic semiconductors | Extrinsic semiconductors | |
| 1) | Semiconductor in the pure form is known as intrinsic semiconductor. |
The semiconductor, resulting from mixing of impurity in it, is known as extrinsic semiconductor |
| 2) | Their conductivity is low | Their conductivity is high. |
| 3) | Its electrical conductivity is a function of temperature alone. |
Its electrical conductivity depends upon the temperature as well as on the quantity of impurity atoms doped in the structure |
| 4) | The number of free electrons in conduction band is equal to the number of holes in valence band. |
In these semiconductors, number of free electrons and number of holes are unequal |
| 5) | These are not practically used | These are practically used |
| 6) | In these, the Fermi energy level lies in the middle of valence band and conduction band. | In these, the Fermi energy level shifts towards valence or conduction energy band. |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The number of silicon atoms per m3 is 5 × 1028. This is doped simultaneously with 5 × 1022 atoms per m3 of Arsenic and 5 × 1020 per m3 atoms of Indium. Calculate the number of electrons and holes. Given that ni= 1.5 × 1016 m−3. Is the material n-type or p-type?
In a p-type semiconductor, the acceptor impurity produces an energy level ______
Electronic configuration of germanium is 2, 8, 18 and 4. To make it extrinsic semiconductor small quantity of antimony is added. The correct statement is ____________.
A donor impurity results in ______.
Semiconductors formed by doping germanium (Ge) with aluminium (Z = 13) and antimony (Z = 51) are ______.
When p-n junction diode is forward biased, then ______.
The electron and hole concentration in a semiconductor in thermal equilibrium is given by ______.
State how a p-type semiconductor will be obtained from a pure crystal of a semiconductor.
Explain the following term:
Extrinsic semiconductor
Distinguish between n-type and p-type semiconductors.
The conductivity of a semiconductor increases with increase in temperature because ______.
Why are elemental dopants for Silicon or Germanium usually chosen from group XIII or group XV?
Sn, C, and Si, Ge are all group XIV elements. Yet, Sn is a conductor, C is an insulator while Si and Ge are semiconductors. Why?
Suppose a ‘n’-type wafer is created by doping Si crystal having 5 × 1028 atoms/m3 with 1 ppm concentration of As. On the surface 200 ppm Boron is added to create ‘P’ region in this wafer. Considering n i = 1.5 × 1016 m–3, (i) Calculate the densities of the charge carriers in the n and p regions. (ii) Comment which charge carriers would contribute largely for the reverse saturation current when diode is reverse biased.
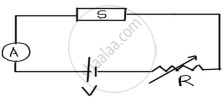
The figure shows a piece of pure semiconductor S in series with a variable resistor R and a source of constant voltage V. Should the value of R be increased or decreased to keep the reading of the ammeter constant, when semiconductor S is heated? Justify your answer
Name the extrinsic semiconductors formed when pure germanium is doped with a trivalent impurity. Draw the energy band diagram of extrinsic semiconductors so formed.
- Statement I: By doping silicon semiconductor with pentavalent material, the electrons density increases.
- Statement II: The n-type semiconductor has net negative charge. In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
Pieces of copper and of silicon are initially at room temperature. Both are heated to temperature T. The conductivity of ______.
- Assertion (A): Putting the p-type semiconductor slab directly in physical contact with the n-type semiconductor slab cannot form the pn junction.
- Reason (R): The roughness at contact will be much more than inter atomic crystal spacing and continuous flow of charge carriers is not possible.
What type of semiconductor is obtained when a crystal of silicon is doped with a trivalent element?
