Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Draw a neat and well labelled diagram of primary reference electrode.
उत्तर
Primary reference electrode:

Standard Hydrogen Electrode
(Primary Reference Electrode)
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The standard e.m.f of the following cell is 0.463 V
`Cu|Cu_(1m)^(++)`
What is the standard potential of Cu electrode?
(A) 1.137 V
(B) 0.337 V
(C) 0.463 V
(D) - 0.463 V
Calculate E°cell for the following reaction at 298 K:
2Al(s) + 3Cu+2(0.01M) → 2Al+3(0.01M) + 3Cu(s)
Given: Ecell = 1.98V
Calculate e.m.f of the following cell at 298 K:
2Cr(s) + 3Fe2+ (0.1M) → 2Cr3+ (0.01M) + 3 Fe(s)
Given: E°(Cr3+ | Cr) = – 0.74 VE° (Fe2+ | Fe) = – 0.44 V
Calculate emf of the following cell at 25 °C :
Fe|Fe2+(0.001 M)| |H+(0.01 M)|H2(g) (1 bar)|Pt (s)
E°(Fe2+| Fe)= −0.44 V E°(H+ | H2) = 0.00 V
Calculate e.m.f. and ∆G for the following cell:
Mg (s) |Mg2+ (0.001M) || Cu2+ (0.0001M) | Cu (s)
`"Given :" E_((Mg^(2+)"/"Mg))^0=−2.37 V, E_((Cu^(2+)"/"Cu))^0=+0.34 V.`
Given the standard electrode potentials,
\[\ce{K+/K}\] = −2.93 V, \[\ce{Ag+/Ag}\] = 0.80 V,
\[\ce{Hg^{2+}/Hg}\] = 0.79 V
\[\ce{Mg^{2+}/Mg}\] = −2.37 V, \[\ce{Cr^{3+}/Cr}\] = −0.74 V
Arrange these metals in their increasing order of reducing power.
In the representation of the galvanic cell, the ions in the same phase are separated by a _______.
Calculate the emf of the following cell at 25°C :
Galvanic or a voltaic cell converts the chemical energy liberated during a redox reaction to ____________.
Standard hydrogen electrode operated under standard conditions of 1 atm H2 pressure, 298 K, and pH = 0 has a cell potential of ____________.
Which cell will measure standard electrode potential of copper electrode?
Use the data given in below find out which of the following is the strongest oxidising agent.
`"E"_("Cr"_2"O"_7^(2-)//"Cr"^(3+))^⊖`= 1.33 V `"E"_("Cl"_2//"Cl"^-)^⊖` = 1.36 V
`"E"_("MnO"_4^-//"Mn"^(2+))^⊖` = 1.51 V `"E"_("Cr"^(3+)//"Cr")^⊖` = - 0.74 V
The positive value of the standard electrode potential of Cu2+/Cu indicates that:
(i) this redox couple is a stronger reducing agent than the H+/H2 couple.
(ii) this redox couple is a stronger oxidising agent than H+/H2 .
(iii) Cu can displace H2 from acid.
(iv) Cu cannot displace H2 from acid.
Value of standard electrode potential for the oxidation of \[\ce{Cl-}\] ions is more positive than that of water, even then in the electrolysis of aqueous sodium chloride, why is \[\ce{Cl-}\] oxidised at anode instead of water?
Which reference electrode is used to measure the electrode potential of other electrodes?
Consider the figure and answer the following question.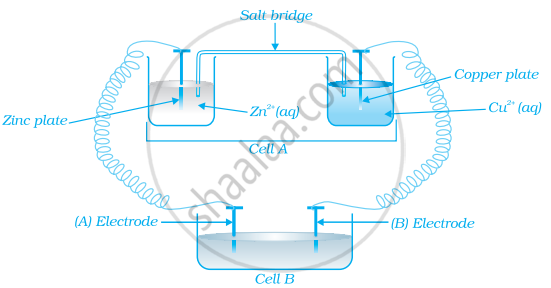
If cell ‘A’ has ECell = 0.5V and cell ‘B’ has ECell = 1.1V then what will be the reactions at anode and cathode?
The standard electrode potential of the two half cells are given below:
\[\ce{Ni^{2+} + 2e^{-} -> Ni, E_0 = - 0.25 Volt}\]
\[\ce{Zn^{2+} + 2e^{-} -> Zn, E_0 = - 0.77 Volt}\]
The voltage of cell formed by combining the two half cells would be?
Which is the correct order of second ionization potential of C, N, O and F in the following?
The potential of a hydrogen electrode at PH = 10 is
The emf of a galvanic cell, with electrode potential of Zn2+ = - 0.76 V and that of Cu2+ = 0.34 V, is ______.
