Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Consider the figure and answer the following question.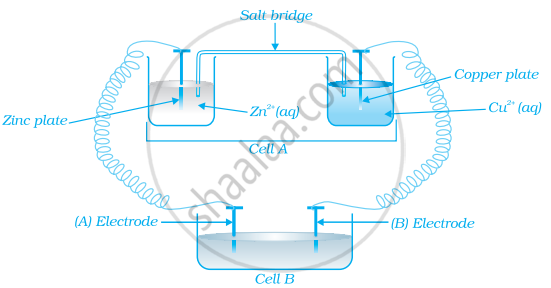
If cell ‘A’ has ECell = 0.5V and cell ‘B’ has ECell = 1.1V then what will be the reactions at anode and cathode?
उत्तर
Now cell ‘B’ acts as galvanic cell as it has higher emf and will push electrons into cell ‘A’.
The electrode reaction will be:
At anode: \[\ce{Zn -> Zn^{2+} + 2e^{-}}\]
At cathode: \[\ce{Cu^{2+} + 2e^{-} -> Cu}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Calculate Ecell and ΔG for the following at 28°C :
Mg(s) + Sn2+( 0.04M ) → Mg2+( 0.06M ) + Sn(s)
E°cell = 2.23V. Is the reaction spontaneous ?
Calculate e.m.f. and ∆G for the following cell:
Mg (s) |Mg2+ (0.001M) || Cu2+ (0.0001M) | Cu (s)
`"Given :" E_((Mg^(2+)"/"Mg))^0=−2.37 V, E_((Cu^(2+)"/"Cu))^0=+0.34 V.`
In the representation of the galvanic cell, the ions in the same phase are separated by a _______.
Draw a neat and labelled diagram of the lead storage battery.
Standard hydrogen electrode operated under standard conditions of 1 atm H2 pressure, 298 K, and pH = 0 has a cell potential of ____________.
The difference between the electrode potentials of two electrodes when no current is drawn through the cell is called ______.
Use the data given in below find out which of the following is the strongest oxidising agent.
`"E"_("Cr"_2"O"_7^(2-)//"Cr"^(3+))^⊖`= 1.33 V `"E"_("Cl"_2//"Cl"^-)^⊖` = 1.36 V
`"E"_("MnO"_4^-//"Mn"^(2+))^⊖` = 1.51 V `"E"_("Cr"^(3+)//"Cr")^⊖` = - 0.74 V
Represent the cell in which the following reaction takes place.The value of E˚ for the cell is 1.260 V. What is the value of Ecell?
\[\ce{2Al (s) + 3Cd^{2+} (0.1M) -> 3Cd (s) + 2Al^{3+} (0.01M)}\]
The potential of a hydrogen electrode at PH = 10 is
A voltaic cell is made by connecting two half cells represented by half equations below:
\[\ce{Sn^{2+}_{ (aq)} + 2e^- -> Sn_{(s)}}\], E0 = − 0.14 V
\[\ce{Fe^{3+}_{ (aq)} + e^- -> Fe^{2+}_{ (aq)}}\], E0 = + 0.77 V
Which statement is correct about this voltaic cell?
