Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Consider the figure and answer the following question.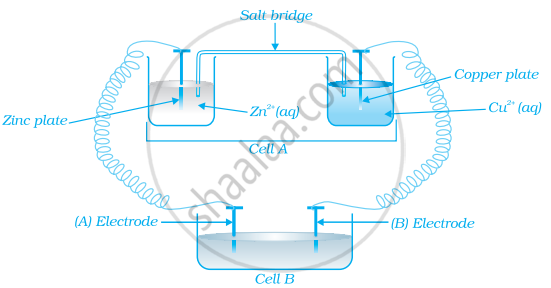
If cell ‘A’ has ECell = 0.5V and cell ‘B’ has ECell = 1.1V then what will be the reactions at anode and cathode?
Solution
Now cell ‘B’ acts as galvanic cell as it has higher emf and will push electrons into cell ‘A’.
The electrode reaction will be:
At anode: \[\ce{Zn -> Zn^{2+} + 2e^{-}}\]
At cathode: \[\ce{Cu^{2+} + 2e^{-} -> Cu}\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Can copper sulphate solution be stored in an iron vessel? Explain.
Calculate the emf of the following cell at 25°C :
Standard electrode potential is measured taking the concentrations of all the species involved in a half-cell is ____________.
Which cell will measure standard electrode potential of copper electrode?
The difference between the electrode potentials of two electrodes when no current is drawn through the cell is called ______.
Using the data given below find out the strongest reducing agent.
`"E"_("Cr"_2"O"_7^(2-)//"Cr"^(3+))^⊖` = 1.33 V `"E"_("Cl"_2//"Cl"^-) = 1.36` V
`"E"_("MnO"_4^-//"Mn"^(2+))` = 1.51 V `"E"_("Cr"^(3+)//"Cr")` = - 0.74 V
Use the data given in below find out which of the following is the strongest oxidising agent.
`"E"_("Cr"_2"O"_7^(2-)//"Cr"^(3+))^⊖`= 1.33 V `"E"_("Cl"_2//"Cl"^-)^⊖` = 1.36 V
`"E"_("MnO"_4^-//"Mn"^(2+))^⊖` = 1.51 V `"E"_("Cr"^(3+)//"Cr")^⊖` = - 0.74 V
Standard electrode potential of three metals X, Y and Z are – 1.2 V, + 0.5 V and – 3.0 V, respectively. The reducing power of these metals will be:
The potential of a hydrogen electrode at PH = 10 is
The emf of a galvanic cell, with electrode potential of Zn2+ = - 0.76 V and that of Cu2+ = 0.34 V, is ______.
