Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Electric charges are distributed in a small volume. The flux of the electric field through a spherical surface of radius 10 cm surrounding the total charge is 25 V m. The flux over a concentric sphere of radius 20 cm will be _____________ .
विकल्प
a
b
c
d
उत्तर
25 V m
The flux through a surface does not depend on its shape and size; it only depends upon the charge enclosed inside the volume. Here, the charge enclosed by the sphere of radius 10 cm and the sphere of radius 20 cm is same so the flux through them will also be same.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
How does the electric flux due to a point charge enclosed by a spherical Gaussian surface get affected when its radius is increased?
Given a uniform electric field `vecE=5xx10^3hati`N/C, find the flux of this field through a square of 10 cm on a side whose plane is parallel to the y-z plane. What would be the flux through the same square if the plane makes a 30° angle with the x-axis ?
What is the net flux of the uniform electric field of previous question through a cube of side 20 cm oriented so that its faces are parallel to the coordinate planes?
Careful measurement of the electric field at the surface of a black box indicates that the net outward flux through the surface of the box is 8.0 × 103 N m2/C.
- What is the net charge inside the box?
- If the net outward flux through the surface of the box were zero, could you conclude that there were no charges inside the box? Why or Why not?
Define Electric Flux. Write its SI unit.
Given a uniform electric field \[\vec{E} = 2 \times {10}^3 \ \hat{i}\] N/C, find the flux of this field through a square of side 20 cm, whose plane is parallel to the y−z plane. What would be the flux through the same square, if the plane makes an angle of 30° with the x−axis ?
Two charges of magnitudes −2Q and +Q are located at points (a, 0) and (4a, 0) respectively. What is the electric flux due to these charges through a sphere of radius ‘3a’ with its centre at the origin?
A small plane area is rotated in an electric field. In which orientation of the area, is the flux of the electric field through the area maximum? In which orientation is it zero?
It is said that any charge given to a conductor comes to its surface. Should all the protons come to the surface? Should all the electrons come to the surface? Should all the free electrons come to the surface?
Choose the correct answer from given options
The electric flux through a closed Gaussian surface depends upon
The electric flux through the surface ______.
 |
 |
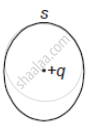 |
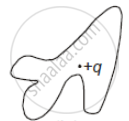 |
| (i) | (ii) | (iii) | (iv) |
The total flux through the faces of the cube with side of length a if a charge q is placed at corner A of the cube is ______.
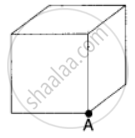
The electric charges are distributed in a small volume. The flux of the electric field through a spherical surface of radius 10 cm surrounding the total charge is 20 V-m. The flux over a concentric sphere of radius 20 cm will be ______.
A hollow sphere of radius R has a point charge Q at its centre. Electric flux emanating from it is `phi`. If both the charge and the radius of the sphere are doubled, electric flux emanating from the sphere will ______.
