Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Electric charges are distributed in a small volume. The flux of the electric field through a spherical surface of radius 10 cm surrounding the total charge is 25 V m. The flux over a concentric sphere of radius 20 cm will be _____________ .
Options
a
b
c
d
Solution
25 V m
The flux through a surface does not depend on its shape and size; it only depends upon the charge enclosed inside the volume. Here, the charge enclosed by the sphere of radius 10 cm and the sphere of radius 20 cm is same so the flux through them will also be same.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
"The outward electric flux due to charge +Q is independent of the shape and size of the surface which encloses is." Give two reasons to justify this statement.
What is the electric flux through a cube of side 1 cm which encloses an electric dipole?
Given the electric field in the region `vecE=2xhati`, find the net electric flux through the cube and the charge enclosed by it.
Given a uniform electric field `vecE=5xx10^3hati`N/C, find the flux of this field through a square of 10 cm on a side whose plane is parallel to the y-z plane. What would be the flux through the same square if the plane makes a 30° angle with the x-axis ?
What is the net flux of the uniform electric field of previous question through a cube of side 20 cm oriented so that its faces are parallel to the coordinate planes?
Careful measurement of the electric field at the surface of a black box indicates that the net outward flux through the surface of the box is 8.0 × 103 N m2/C.
- What is the net charge inside the box?
- If the net outward flux through the surface of the box were zero, could you conclude that there were no charges inside the box? Why or Why not?
Given a uniform electric field \[\vec{E} = 2 \times {10}^3 \ \hat{i}\] N/C, find the flux of this field through a square of side 20 cm, whose plane is parallel to the y−z plane. What would be the flux through the same square, if the plane makes an angle of 30° with the x−axis ?
A charge q is placed at the centre of the open end of a cylindrical vessel (see the figure). The flux of the electric field through the surface of the vessel is ____________ .

The following figure shows a closed surface that intersects a conducting sphere. If a positive charge is placed at point P, the flux of the electric field through the closed surface

Choose the correct answer from given options
The electric flux through a closed Gaussian surface depends upon
Total electric flux coming out of a unit positive charge kept in air is ______.
A charge Qµc is placed at the centre of a cube the flux coming from any surface will be.
An electric charge q is placed at the center of a cube of side ℓ. The electric flux on one of its faces will be ______.
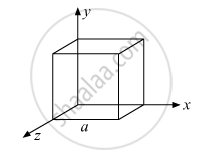
What will be the total flux through the faces of the cube (figure) with side of length a if a charge q is placed at

- A: a corner of the cube.
- B: mid-point of an edge of the cube.
- C: centre of a face of the cube.
- D: mid-point of B and C.
A hollow sphere of radius R has a point charge Q at its centre. Electric flux emanating from it is `phi`. If both the charge and the radius of the sphere are doubled, electric flux emanating from the sphere will ______.
A hollow sphere of radius R has a point charge q at its centre. Electric flux emanating from the sphere is X. How will the electric flux change, if at all, when radius of the sphere is doubled?
