Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain Bredig’s arc method.
उत्तर
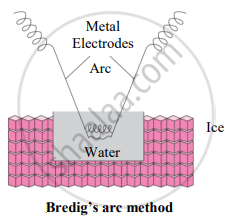
- Colloidal sols can be prepared by electrical disintegration using Bredig’s arc method.
- This process involves vaporization as well as condensation.
- Colloidal sols of metals such as gold, silver, platinum can be prepared by this method.
- In this method, an electric arc is struck between electrodes of metal immersed in the dispersion medium.
- The intense heat produced vapourizes the metal which then condenses to form particles of colloidal sol.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write one difference in Multimolecular colloid and Associated colloid
Define the following with a suitable example, of each:
Multimolecular colloid
Choose the correct option.
The size of colloidal particles lies between ______.
Define the term Electrophoresis.
Write a note on the Tyndall effect.
Explain Electrophoresis diagramatically.
Draw labelled diagram of Soap micelle.
Which type of colloid is formed on the dissolution of soap in water?
Which one of the following methods is used to make platinum sol?
Maximum coagulation power is in ____________.
Which of the following ionic species has highest precipitating power?
In which of the following sols there is low affinity between dispersed phase and dispersion medium?
Some colloids are stable by their nature, i.e., gels, alloys, and solid foams. Gelatin and jellies are two common examples of a gel. The solid and liquid phases in a gel are interdispersed with both phases being continuous. In most systems, the major factor influencing the stability is the charge on the colloidal particles. If a particular ion is preferentially adsorbed on the surface of the particles, the particles in suspension will repel each other, thereby preventing the formation of aggregates that are larger than colloidal dimensions. The ion can be either positive or negative depending on the particular colloidal system, i.e., air bubbles accumulate negative ions, sulphur particles have a net negative charge in a sulphur sol, and the particles in a metal hydroxide sol are positively charged. Accumulation of charge on a surface is not an unusual phenomenon-dust is attracted to furniture surfaces by electrostatic forces. When salts are added to lyophobic colloidal systems the colloidal particles begin to form larger aggregates and a sediment forms as they settle. This phenomenon is called flocculation, and the suspension can be referred to as flocculated, or colloidally unstable. If the salt is removed, the suspension can usually be restored to its original state; this process is called deflocculation or peptization. The original and restored colloidal systems are called deflocculated, peptized, or stable sols.
Why does a small amount of salt have such a dramatic effect on the stability of a lyophobic colloidal system? The answer lies in an understanding of the attractive and repulsive forces that exist between colloidal particles. Van der Waals forces are responsible for the attractions, while the repulsive forces are due to the surface charge on the particles. In a stable colloid, the repulsive forces are of greater magnitude than the attractive forces. The magnitude of the electrical repulsion is diminished by addition of ionized salt, which allows the dispersed particles to aggregate and flocculate. River deltas provide an example of this behaviour. A delta is formed at the mouth of a river because the colloidal clay particles are flocculated when the freshwater mixes with the salt water of the ocean.
Gelatin is a _________ colloidal system.
Which of the following electrolytes will have maximum coagulating value for AgI/Ag+ solution?
An emulsion cannot be broken by:
(i) heating
(ii) adding more amount of dispersion medium
(iii) freezing
(iv) adding emulsifying agent
What is collodion?
What happens when electric field is applied to colloidal solution?
How do emulsifying agents stabilise the emulsion?
On the basis of Hardy-Schulze rule explain why the coagulating power of phosphate is higher than chloride.
Toluene is oxidised to benzoic acid by
Cloud is an example of
The coagulation of 200 ML of position sol took place when 0.73 HCL was added to its without changing the volume much. The flocculation value of HCL for the colloid is.
In which of the following, the Tyndall effect is not observed?
Van Arkel's method of purification of metals involves converting the metal to a ______.
Starch is an example of which of the following type of colloid?
Identify positively charged sol from following.
Identify the correct decreasing order of precipitation power of flocculating ion added, from following.
