Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the following term:
Substitutional impurity defect
उत्तर
Substitutional impurity defect: In this defect, the foreign atoms are found at the lattice sites in place of host atoms. The regular atoms are displaced from their lattice sites by impurity atoms.
For example :
- Solid solutions of metals (alloys): Brass is an alloy of Cu and Zn. In brass, host Cu atoms are replaced by the impurity of Zn atoms. The Zn atoms occupy regular sites of Cu atoms as shown in the figure.
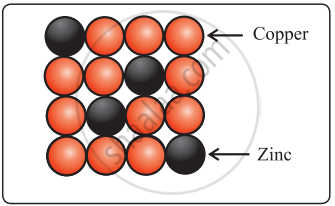 Brass Brass |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What are the consequences of Schottky defect?
Explain with diagram, the vacancy defect.
What is a substitutional impurity defect?
Explain solid solutions of metals and vacancy through aliovalent cations.
Which of the following is an example of substitutional impurity defect?
When a cation or anion from ionic solid leaves its regular lattice site and moves to occupy an interstitial site, it is called as ____________.
Which among the following solids shows Frenkel defect?
Which of the following match is CORRECT?
(I) Frenkel defect: Electrical neutrality of the compound is preserved.
(II) Schottky defect: Density of the substance decreases.
(III) Schottky defect: Combination of vacancy defect and interstitial defect.
(IV) Frenkel defect: Small difference between size of cation and anion.
Which among the following statements is true about Schottky defect?
Which of the following pair of ionic crystals show Schottky defect?
Schottky defect in crystals is observed when ____________.
Which among the following defects is observed in Brass?
Write the consequences of Schottky defect with reasons.
In which among the following solids, Schottky defect is not observed?
When electrons are trapped into the crystal in anion vacancy, the defect is known as ______.
Explain Self interstitial defect in elemental solid.
What is a crystal defect?
What is a vacancy defect?
Give the disadvantages of a vacancy defect.
What are point defects?
