Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Find a vector \[\overrightarrow{a}\] of magnitude \[5\sqrt{2}\], making an angle of \[\frac{\pi}{4}\] with x-axis, \[\frac{\pi}{2}\] with y-axis and an acute angle θ with z-axis.
उत्तर
It is given that vector \[\overrightarrow{a}\] makes an angle of \[\frac{\pi}{4}\] with x-axis, \[\frac{\pi}{2}\] with y-axis and an acute angle θ with z-axis.
\[\therefore l = \cos\frac{\pi}{4} = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}, m = \cos\frac{\pi}{2} = 0, n = \cos\theta\]
Now,
\[l^2 + m^2 + n^2 = 1\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{1}{2} + 0 + \cos^2 \theta = 1\]
\[ \Rightarrow \cos^2 \theta = 1 - \frac{1}{2} = \frac{1}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \cos\theta = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \left( \theta\text{ is acute }\right)\]
We know that
\[\overrightarrow{a} = \left| \overrightarrow{a} \right|\left( l \hat{i} + m \hat{j} + n \hat{k} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \overrightarrow{a} = 5\sqrt{2}\left( \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \hat{i} + 0 \hat{j} + \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \hat{k} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \overrightarrow{a} = 5\left( \hat{i} + 0 \hat{j} + \hat{k} \right)\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Find a vector `veca` of magnitude `5sqrt2` , making an angle of `π/4` with x-axis, `π/2` with y-axis and an acute angle θ with z-axis.
Find the magnitude of two vectors `veca and vecb`, having the same magnitude and such that the angle between them is 60° and their scalar product is `1/2`.
If `veca` is a nonzero vector of magnitude 'a' and λ a nonzero scalar, then λ`veca` is unit vector if ______.
If `veca, vecb, vecc` are mutually perpendicular vectors of equal magnitudes, show that the vector `veca + vecb+ vecc` is equally inclined to `veca, vecb` and `vecc`.
If `veca, vecb, vecc` are mutually perpendicular vectors of equal magnitudes, find the angle which `veca + vecb + vecc`make with `veca or vecb or vecc`
Represent the following graphically:
(i) a displacement of 40 km, 30° east of north
(ii) a displacement of 50 km south-east
(iii) a displacement of 70 km, 40° north of west.
Find the magnitude of the vector \[\vec{a} = 2 \hat{i} + 3 \hat{j} - 6 \hat{k} .\]
If the sum of two unit vectors is a unit vector prove that the magnitude of their difference is `sqrt(3)`.
If \[\vec{a} = \hat{i} + \hat{j} + \hat{k} , \vec{b} = 4 \hat{i} - 2 \hat{j} + 3 \hat{k} \text { and } \vec{c} = \hat{i} - 2 \hat{j} + \hat{k} ,\] find a vector of magnitude 6 units which is parallel to the vector \[2 \vec{a} - \vec{b} + 3 \vec{c .}\]
Find a vector of magnitude of 5 units parallel to the resultant of the vectors \[\vec{a} = 2 \hat{i} + 3 \hat{j} - \hat{k} \text{ and } \vec{b} = \hat{i} - 2 \hat{j} +\widehat{k} .\]
A vector \[\vec{r}\] is inclined at equal angles to the three axes. If the magnitude of \[\vec{r}\] is \[2\sqrt{3}\], find \[\vec{r}\].
Write a vector of magnitude 12 units which makes 45° angle with X-axis, 60° angle with Y-axis and an obtuse angle with Z-axis.
Write the length (magnitude) of a vector whose projections on the coordinate axes are 12, 3 and 4 units.
Find a vector in the direction of \[\overrightarrow{a} = 2 \hat{i} - \hat{j} + 2 \hat{k} ,\] which has magnitude of 6 units.
Write two different vectors having same magnitude.
Write a vector in the direction of vector \[5 \hat{i} - \hat{j} + 2 \hat{k}\] which has magnitude of 8 unit.
Find a vector in the direction of vector \[2 \hat{i} - 3 \hat{j} + 6 \hat{k}\] which has magnitude 21 units.
If in a ∆ABC, A = (0, 0), B = (3, 3 \[\sqrt{3}\]), C = (−3\[\sqrt{3}\], 3), then the vector of magnitude 2 \[\sqrt{2}\] units directed along AO, where O is the circumcentre of ∆ABC is
Prove that in a ∆ABC, `sin"A"/"a" = sin"B"/"b" = sin"C"/"c"`, where a, b, c represent the magnitudes of the sides opposite to vertices A, B, C, respectively.
The magnitude of the vector `6hat"i" + 2hat"j" + 3hat"k"` is ______.
A vector `vec"r"` is inclined at equal angles to the three axes. If the magnitude of `vec"r"` is `2sqrt(3)` units, find `vec"r"`.
Two equal forces acting at a point with an angle of 60° between them, if the resultant is equal `30sqrt(3)N`, the magnitude of the force will be
The area under a velocity-time curve represents the change in ______?
Which of the following statements is false about forces/ couple?
The magnitude of the vector `6hati - 2hatj + 3hatk` is ______.
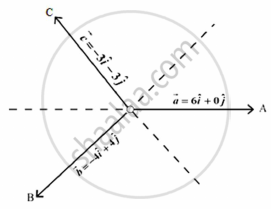
Read the following passage and answer the questions given below:
|
Teams A, B, C went for playing a tug of war game. Teams A, B, C have attached a rope to a metal ring and is trying to pull the ring into their own area. Team A pulls with force F1 = `6hati + 0hatj kN`, Team B pulls with force F2 = `-4hati + 4hatj kN`, Team C pulls with force F3 = `-3hati - 3hatj kN`,
|
- What is the magnitude of the force of Team A ?
- Which team will win the game?
- Find the magnitude of the resultant force exerted by the teams.
OR
In what direction is the ring getting pulled?
Find a vector of magnitude 20 units parallel to the vector `2hati + 5hatj + 4hatk`.