Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Give reason for the higher boiling point of ethanol in comparison to methoxymethane.
उत्तर
Ethanol undergoes intermolecular H-bonding due to the presence of −OH group, resulting in the association of molecules. Extra energy is required to break these hydrogen bonds. On the other hand, methoxymethane does not undergo H-bonding. Therefore, ethanol has a higher boiling point than methoxymethane.
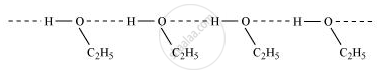
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain why propanol has higher boiling point than that of the hydrocarbon, butane?
Arrange the following compounds in the increasing order of their acid strength:
p-cresol, p-nitrophenol, phenol
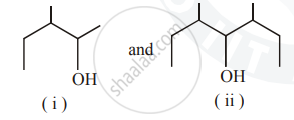
Identify the chiral molecule in the following pair :
Write the structures of A, B and C in the following reactions :
\[ C_6 H_5 {NO}_2 \to^{Sn/HCI} A \to^{{NaNO}_2 /HCI}_{273 K} B \to^{H_2 O}_∆ C\]
Account for the following:
CH3CHO is more reactive than CH3COCH3 towards reaction with HCN.
Alcohols have high boiling points because of ____________.
Alcohols of low molecular weight are _____________.
Which of the following has lowest boiling point?
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of boiling point. Propan-1-ol, butan-1-ol, butan-2-ol, pentan-1-ol
Explain why alcohols and ethers of comparable molecular mass have different boiling points?
Assertion: Boiling points of alcohols and ethers are high.
Reason: They can form intermolecular hydrogen-bonding.
A solution of phenol in chloroform when treated with aqueous NaOH gives compound P as a major product. The mass percentage of carbon in P is ______. (to the nearest integer) (Atomic mass: C = 12; H = 1; O = 16)
Arrange the following in order of increasing boiling point:
Ethoxyethane, Butanal, Butanol, n-butane
How are the following conversion carried out?
Methyl magnesium bromide →2-Methylpropan-2-ol.
What is esterifications? How is an ester obtained from alcohol or phenol?
How are the following conversions carried out?
Methyl magnesium bromide → 2 -Methylpropan-2-ol.
How are the following conversions carried out?
\[\ce{Methyl magnesium bromide -> 2-Methylpropan-2-ol}\]
How is the following conversion carried out?
\[\ce{Methyl magnesium bromide ->2-Methylpropan-2-ol}\]
