Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Given the following data for incident wavelength and the stopping potential obtained from an experiment on the photoelectric effect, estimate the value of Planck's constant and the work function of the cathode material. What is the threshold frequency and corresponding wavelength? What is the most likely metal used for emitter?
| Incident wavelength (in Å) | 2536 | 3650 |
| Stopping potential (in V) |
1.95 | 0.5 |
उत्तर
Data: λ = 2536 Å = 2.536 × 10-7 m,
λ' = 3650 Å = 3.650 × 10-7 m,
V0 = 1.95 V, V0' = 0.5 V, c = 3 × 108 m/s,
e = 1.6 × 10-19 C
(i) `"V"_0"e" = "hc"/lambda - phi and "V"_0'"e" = "hc"/(lambda') - phi`
∴ `("V"_0 - "V"_0')"e" = "hc" (1/lambda - 1/(lambda '))`
∴ (1.95 - 0.5)(1.6 × 10-19)
= h (3 × 108)`(10^7/2.536 - 10^7/3.650)`
∴ 2.32 × 10-19 = h(3 × 1015)(0.3943 - 0.2740)
∴ h = `(2.32 xx 10^(-34))/0.3609 = 6.428 xx 10^(-34)` J.s
This is the value of Planck's constant.
(ii) `phi = "hc"/lambda - "V"_0"e"`
`= ((6.428 xx 10^-34)(3 xx 10^8))/(2.536 xx 10^-7) - (1.95)(1.6 xx 10^-19)`
`= 7.604 xx 10^-19 - 3.12 xx 10^-19 = 4.484 xx 10^-19`J
`= (4.484 xx 10^-19"J")/(1.6 xx 10^-19 "J"//"eV")`
= 2.803 eV
This the work function of the cathode material.
(iii) Φ = hv0
∴ The threshold frequency, `"v"_0 = phi/"h"`
`= (4.484 xx 10^-19 "J")/(6.428 xx 10^-34 "J.s") = 6.976 xx 10^14` Hz
(iv) `"v"_0 = "c"/lambda_0`
∴ The threshold wavelength, `lambda_0 = "c"/"v"_0`
`= (3 xx 10^8)/(6.976 xx 10^14) = 4.300 xx 10^-7` = 4300 Å
(v) The most likely metal used for emitter: calcium.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Choose the correct option.
Polychromatic (containing many different frequencies) radiation is used in an experiment on the photoelectric effect. The stopping potential ______.
Using the values of work function given in the following table, tell which metal will require the highest frequency of incident radiation to generate photocurrent.
Typical values of work function for some common metals
| Metal | Work function (in eV) |
| Potassium | 2.3 |
| Sodium | 2.4 |
| Calcium | 2.9 |
| Zinc | 3.6 |
| Silver | 4.3 |
| Aluminium | 4.3 |
| Tungsten | 4.5 |
| Copper | 4.7 |
| Nickel | 5.0 |
| Gold | 5.1 |
It is observed in an experiment on the photoelectric effect that an increase in the intensity of the incident radiation does not change the maximum kinetic energy of the electrons. Where does the extra energy of the incident radiation go? Is it lost? State your answer with explanatory reasoning.
Radiation of wavelength 4500 Å is incident on a metal having work function 2.0 eV. Due to the presence of a magnetic field B, the most energetic photoelectrons emitted in a direction perpendicular to the field move along a circular path of radius 20 cm. What is the value of the magnetic field B?
Planck's constant is 6.6 × 10-34 Js. The momentum of each photon is given radiation Is 3.3 × 10-29 kg/s. The λ of radiation is ______.
Define photoelectric effect.
Find the kinetic energy of the emitted electron, if in photoelectric effect energy of incident Photon is 4 eV and work function is 2.4 eV.
Explain the concept of the photoelectric effect.
The ratio of energies of photons produced due to transition of electron of hydrogen atom from its (i) second to first energy level and (ii) highest energy level to second level is respectively.
Which one of the following is TRUE in photoelectric emission?
Photoelectrons emitted from a metallic surface are initially ____________.
An important spectral emission line has a wavelength of 21 cm. The corresponding photon energy is (h = 6.62 x 10-34 Js, c = 3 x 108 m/s) ____________.
The threshold frequency for a certain photosensitive metal is v0. When it is illuminated by light of frequency v = 2v0, the maximum velocity of photoelectrons is v0. What will be the maximum velocity of the photoelectrons when the same metal is illuminated by light of frequency
v = 5v0?
In photoelectric effect, for a light of different intensities but of same frequency, the stopping potential for a given metal is ____________.
A metal surface is illuminated by photons of energy 5 eV and 2.5 eV respectively. The ratio of their wavelengths is ____________.
When light of wavelength 'λ' is incident on a photosensitive surface, the stopping potential is 'V'. When light of wavelength '3λ' is incident on the same surface, the stopping potential is `"V"/6`. Threshold wavelength for the surface is _______.
The lowest frequency of light that will cause the emission of photoelectrons from the surface of a metal (for which work function is 1.65 eV) will be ____________.
The radiations of energies 1 eV and 2.5 eV are incident on a metal surface having work function 0.5 eV. The ratio of the maximum velocities of the emitted photo-electrons is ____________.
When a photosensitive surface is irradiated by lights of wavelengths `lambda_1` and `lambda_2`, kinetic energies of emitted photoelectrons are E1 and E2 respectively. The work function of the photosensitive surface is ____________.
Two incident radiations having energies two times and ten times of the work function of a metal surface, produce photoelectric effect. The ratio of maximum velocities of emitted photo electrons respectively is ____________.
An electromagnetic wave of wavelength '`lambda`' is incident on a photosensitive surface of negligible work function. If the photoelectrons emitted from this surface have the de-Broglie wavelength '`lambda_1`' then ____________.
The ratio of slopes m1: ro2 of the lines given in the following graphs is, ______.
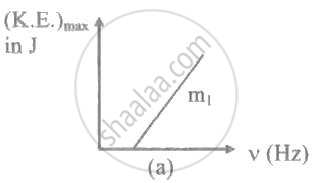
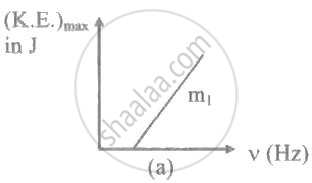
The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons ejected will be ______ eV when the light of wavelength 350 nm is incident on a cesium surface. The work function of cesium = 1.9 eV.
Two radiations of photons energies 1 eV and 2.5 eV, successively illuminate a photosensitive metallic surface of work function 0.5 eV. The ratio of the maximum speeds of the emitted electrons is ______.
If the electron in hydrogen atom jumps from second Bohr orbit to ground state and difference between energies of the two states is radiated in the form of photons. If the work function of the material is 4.2 eV, then stopping potential is ______.
[Energy of electron in nth orbit = `-13.6/"n"^2` eV ]
Draw a neat labelled diagram of photo-current as a function of accelerating potential for fixed incident intensity but different incident frequencies for the same emitter material.
In a photoelectric experiment, the stopping potential is 1.5V. What is the maximum kinetic energy of a photoelectron?
