Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
How does an unpolarized light incident on a polaroid get polarized? Describe briefly, with the help of a necessary diagram, the polarization of light by reflection from a transparent medium.
उत्तर
Polaroid is made up of a special material which blocks one of the two planes of vibration of an electromagnetic wave. Because of its chemical composition it allows only those vibrations of the electromagnetic wave which are parallel to its crystallographic axis.

An ordinary beam of light on reflection from a transparent medium becomes partially polarised. The degree of polarisation increases as the angle of incidence is increased. At a particular value of angle of incidence, the reflected beam becomes completely polarised. This angle of incidence is called the polarising angle (p).
संबंधित प्रश्न
In Young's double slit experiment, plot a graph showing the variation of fringe width versus the distance of the screen from the plane of the slits keeping other parameters same. What information can one obtain from the slope of the curve?
In Young's double slit experiment, using monochromatic light of wavelength λ, the intensity of light at a point on the screen where path difference is λ, is K units. Find out the intensity of light at a point where path difference is `λ/3`.
In Young’s double slit experiment to produce interference pattern, obtain the conditions for constructive and destructive interference. Hence deduce the expression for the fringe width.
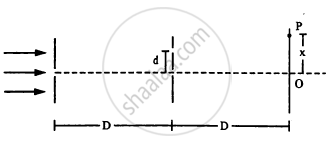
Consider the arrangement shown in the figure. The distance D is large compared to the separation d between the slits.
- Find the minimum value of d so that there is a dark fringe at O.
- Suppose d has this value. Find the distance x at which the next bright fringe is formed.
- Find the fringe-width.
In Young’s double-slit experiment, using monochromatic light, fringes are obtained on a screen placed at some distance from the slits. If the screen is moved by 5 x 10-2 m towards the slits, the change in the fringe width is 3 x 10-5 m. If the distance between the two slits is 10-3 m, calculate the wavelength of the light used.
Two balls are projected at an angle θ and (90° − θ) to the horizontal with the same speed. The ratio of their maximum vertical heights is:
In Young's double slit experiment, the minimum amplitude is obtained when the phase difference of super-imposing waves is: (where n = 1, 2, 3, ...)
In a Young’s double slit experiment, the source is white light. One of the holes is covered by a red filter and another by a blue filter. In this case ______.
Consider a two-slit interference arrangement (Figure) such that the distance of the screen from the slits is half the distance between the slits. Obtain the value of D in terms of λ such that the first minima on the screen falls at a distance D from the centre O.
How will the interference pattern in Young's double-slit experiment be affected if the phase difference between the light waves emanating from the two slits S1 and S2 changes from 0 to π and remains constant?
