Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If (– 4, 3) and (4, 3) are two vertices of an equilateral triangle, find the coordinates of the third vertex, given that the origin lies in the interior of the triangle.
उत्तर
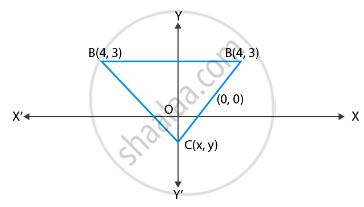
Let the vertices be (x, y)
Distance between (x, y) and (4, 3) is = `sqrt((x - 4)^2 + (y - 3)^2)` ...(1)
Distance between (x,y) and (– 4, 3) is = `sqrt((x + 4)^2 + (y - 3)^2)` ...(2)
Distance between (4, 3) and (– 4, 3) is = `sqrt((4 + 4)^2 + (3 - 3)^2) = sqrt(8)^2`= 8
According to the question,
Equation (1) = (2)
(x – 4)2 = (x + 4)2
x2 – 8x + 16 = x2 + 8x + 16
16x = 0
x = 0
Also, equation (1) = 8
(x – 4)2 + (y – 3)2 = 64 ...(3)
Substituting the value of x in (3)
Then (0 – 4)2 + (y – 3)2 = 64
(y – 3)2 = 64 – 16
(y – 3)2 = 48
y – 3 = `(+)4sqrt(3)`
y = `3(+) 4sqrt(3)`
Neglect y = `3(+) 4sqrt(3)` as if y = `3(+) 4sqrt(3)` then origin cannot interior of triangle
Therefore, the third vertex = `(0, 3 - 4sqrt(3))`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Find the coordinates of the centre of the circle passing through the points (0, 0), (–2, 1) and (–3, 2). Also, find its radius.
Find the distance between the following pairs of points:
(a, b), (−a, −b)
Find the distance of the following point from the origin :
(5 , 12)
Find the distance between P and Q if P lies on the y - axis and has an ordinate 5 while Q lies on the x - axis and has an abscissa 12 .
Find the coordinate of O , the centre of a circle passing through P (3 , 0), Q (2 , `sqrt 5`) and R (`-2 sqrt 2` , -1). Also find its radius.
Find the distance between the points (a, b) and (−a, −b).
Show that (-3, 2), (-5, -5), (2, -3) and (4, 4) are the vertices of a rhombus.
Find the point on y-axis whose distances from the points A (6, 7) and B (4, -3) are in the ratio 1: 2.
Find the distance of the following points from origin.
(a+b, a-b)
Calculate the distance between A (7, 3) and B on the x-axis, whose abscissa is 11.
