Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If all matters were made of electrically neutral particles such as neutrons,
(a) there would be no force of friction
(b) there would be no tension in the string
(c) it would not be possible to sit on a chair
(d) the earth could not move around the sun.
उत्तर
(a) there would be no force of friction
(b) there would be no tension in the string
(c) it would not be possible to sit on a chair
For the existence of friction between two bodies and tension in a string, electromagnetic force is needed. Electromagnetic force exists only between charged particles. For sitting on a chair, we need fractional force. A neutral particle can exert gravitational force on other neutral particles. So, even if all the matters were made up of electrically neutral particles, the earth will still move around the sun.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A lawyer alleges in court that the police had forced his client to issue a statement of confession. What kind of force is this ?
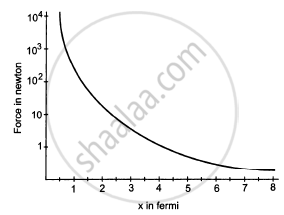
Suppose the magnitude of Nuclear force between two protons varies with the distance between them as shown in figure. Estimate the ratio "Nuclear force/Coulomb force" for
(a) x = 8 fm
(b) x = 4 fm
(c) x = 2 fm
(d) x = 1 fm (1 fm = 10 −15m).
A neutron exerts a force on a proton which is
(a) gravitational
(b) electromagnetic
(c) nuclear
(d) weak
A proton exerts a force on a proton which is
(a) gravitational
(b) electromagnetic
(c) nuclear
(d) weak
Mark the correct statements :
(a) The nuclear force between two protons is always greater than the electromagnetic force between them.
(b) The electromagnetic force between two protons is always greater than the gravitational force between them.
(c) The gravitational force between two protons may be greater than the nuclear force between them.
(d) Electromagnetic force between two protons may be greater than the nuclear force acting between them.
Which of the following systems may be adequately described by classical physics ?
(a) motion of a cricket ball
(b) motion of a dust particle
(c) a hydrogen atom
(d) a neutron changing to a proton.
The gravitational force acting on a particle of 1 g due to a similar particle is equal to 6.67 × 10−17 N. Calculate the separation between the particles.
Calculate the force with which you attract the earth.
A monkey is sitting on a tree limb. The limb exerts a normal force of 48 N and a frictional force of 20 N. Find the magnitude of the total force exerted by the limb on the monkey.
Find the ratio of the magnitude of the electric force to the gravitational force acting between two protons.
A block of mass m slides down a smooth vertical circular track. During the motion, the block is in
A particle is acted upon by a force of constant magnitude which is always perpendicular to the velocity of the plane. The motion of the particle takes place in a plane. It follows that
(a) its velocity is constant
(b) its acceleration is constant
(c) its kinetic energy is constant
(d) it moves in a circular path.
No work is done by a force on an object if
(a) the force is always perpendicular to its velocity
(b) the force is always perpendicular to its acceleration
(c) the object is stationary but the point of application of the force moves on the object
(d) the object moves in such a way that the point of application of the force remains fixed.
A force \[F = \alpha + bx\] acts on a particle in the x-direction, where a and b are constants. Find the work done by this force during a displacement from x = 0 to x = d.
Find the average frictional force needed to stop a car weighing 500 kg at a distance of 25 m if the initial speed is 72 km/h.
Find the average force needed to accelerate a car weighing 500 kg from rest to 72 km/h through a distance of 25 m.
A block of mass 2 kg kept at rest on an inclined plane of inclination 37° is pulled up the plane by applying a constant force of 20 N parallel to the incline. The force acts for one second. Show that the work done by the applied force does not exceed 40 J.
A uniform chain of mass m and length l overhangs a table with its two third part on the table. Find the work to be done by a person to put the hanging part back on the table.
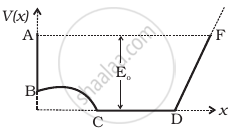
A graph of potential energy V(x) verses x is shown in figure. A particle of energy E0 is executing motion in it. Draw graph of velocity and kinetic energy versus x for one complete cycle AFA.