Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If one angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the other two angles, then the triangle is
विकल्प
an isosceles triangle
an obtuse triangle
an equilateral triangle
a right triangle
उत्तर
In the given problem, one angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the other two angles.
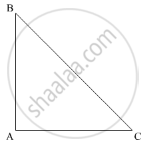
Thus,
∠A = ∠B + ∠C ..........(1)
Now, according to the angle sum property of the triangle
In ΔABC
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180°
∠B + ∠C +∠B + ∠C = 180°
2(∠B + ∠C ) = 180°
`∠B + ∠C = (180°)/2 `
∠B + ∠C = 90° .........(2)
Further, using (2) in (1),
∠A = ∠B + ∠C
∠A = 90°
Thus, ∠A = 90°
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
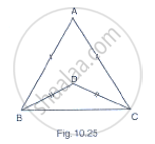
In Fig. 10.25, AB = AC and DB = DC, find the ratio ∠ABD : ∠ACD.
State exterior angle theorem.
State, if the triangle is possible with the following angles :
40°, 130°, and 20°
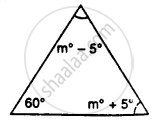
Find the unknown marked angles in the given figure:
Find x, if the angles of a triangle is:
x°, x°, x°
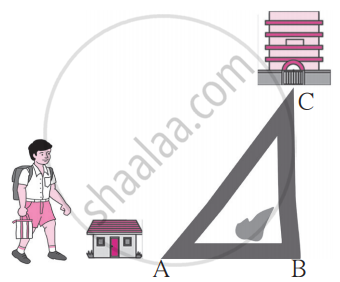
As shown in the figure, Avinash is standing near his house. He can choose from two roads to go to school. Which way is shorter? Explain why.
The length of the three segments is given for constructing a triangle. Say whether a triangle with these sides can be drawn. Give the reason for your answer.
17 cm, 7 cm, 8 cm
In the given figure, AB is parallel to CD. Then the value of b is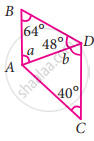
Prove that in a triangle, other than an equilateral triangle, angle opposite the longest side is greater than `2/3` of a right angle.
Can we have two acute angles whose sum is an obtuse angle? Why or why not?
