Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If the sides of a triangle are 3 cm, 4 cm and 5 cm, then the area is
विकल्प
3 cm2
6 cm2
9 cm2
12 cm2
उत्तर
6 cm2
Explanation;
Hint:
a = 3 cm, b = 4 cm, c = 5 cm
s = `("a" + "b" + "c")/2`
= `(3 + 4 + 5)/2`
= 6 cm
Area of the triangle = `sqrt("s"("s" - "a")("s" - "b")("s" - "c"))`
= `sqrt(6 xx 3 xx 2 xx 1)`
= `sqrt(36)`
= 6 cm2
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Find the area of the triangle ABC with A(1, −4) and mid-points of sides through A being (2, −1) and (0, −1).
Find the area of the triangle whose vertices are: (2, 3), (-1, 0), (2, -4)
Show that points A (a, b + c), B (b, c + a), C (c, a + b) are collinear.
Prove that the points (a, 0), (0, b) and (1, 1) are collinear if `1/a+1/b=1`
Prove analytically that the line segment joining the middle points of two sides of a triangle is equal to half of the third side.
Show that the points are the vertices of an isosceles right triangle.
In a triangle ABC, if `|(1, 1, 1),(1 + sin"A", 1 + sin"B", 1 + sin"C"),(sin"A" + sin^2"A", sin"B" + sin^2"B", sin"C" + sin^2"C")|` = 0, then prove that ∆ABC is an isoceles triangle.
Find the coordinates of the point Q on the x-axis which lies on the perpendicular bisector of the line segment joining the points A(–5, –2) and B(4, –2). Name the type of triangle formed by the points Q, A and B.
Find the missing value:
| Base | Height | Area of parallelogram |
| ______ | 8.4 cm | 48.72 cm2 |
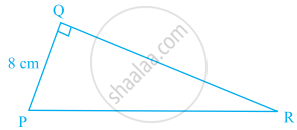
Area of a triangle PQR right-angled at Q is 60 cm2 in the figure. If the smallest side is 8 cm long, find the length of the other two sides.