Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In the following figure, BDEF and DCEF are each a parallelogram. Is it true that BD = DC? Why or why not?
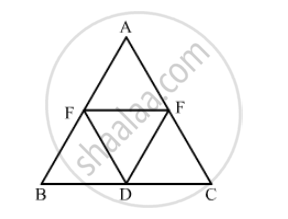
उत्तर
\[\text{ In parallelogram BDEF }\]
\[ \therefore BD = EF . . . (i) (\text{ opposite sides of a parallelogram are equal })\]
\[\text{ In parallelogram DCEF }\]
\[ CD = EF . . . (ii) (\text{ opposite sides of a parallelogram are equal })\]
\[\text{ From equations (i) and } (ii)\]
\[BD = CD\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain why a rectangle is a convex quadrilateral.
Two adjacent angles of a parallelogram are (3x − 4)° and (3x + 10)°. Find the angles of the parallelogram.
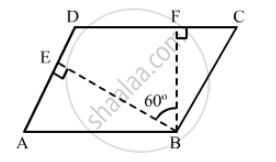
The angle between the altitudes of a parallelogram, through the same vertex of an obtuse angle of the parallelogram is 60°. Find the angles of the parallelogram.
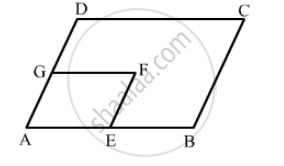
In the following figure, ABCD and AEFG are parallelograms. If ∠C = 55°, what is the measure of ∠F?
Which of the following statement is true for a rectangle?
Its diagonals are equal and perpendicular, and bisect each other.
Fill in the blank of the following, so as to make the statement true:
A square is a rectangle in which .....
A mason has made a concrete slab. He needs it to be rectangular. In what different ways can he make sure that it is rectangular?
A quadrilateral whose opposite sides and all the angles are equal is a ______.
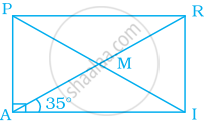
In rectangle PAIR, find ∠ARI, ∠RMI and ∠PMA.
Quadrilateral EFGH is a rectangle in which J is the point of intersection of the diagonals. Find the value of x if JF = 8x + 4 and EG = 24x – 8.
