Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
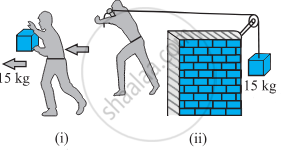
In Figure (i) the man walks 2 m carrying a mass of 15 kg on his hands. In Figure (ii), he walks the same distance pulling the rope behind him. The rope goes over a pulley, and a mass of 15 kg hangs at its other end. In which case is the work done greater?
उत्तर
In Fig. (i), the force is applied horizontally, and the movement is also along the horizontal plane.
θ = 90°
W = Fs cos 90° = zero
In Fig. (ii), the force is applied in a horizontal direction, and the movement occurs horizontally as well.
Therefore, θ = 0°.
W = Fs cos θ = mg x s cos 0°
W = 15 x 9.8 x 2 x 1 = 294 joule.
Thus, work done in (ii) case is greater.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Consider the situation of the previous question from a frame moving with a speed v0 parallel to the initial velocity of the block. (a) What are the initial and final kinetic energies? (b) What is the work done by the kinetic friction?
A small block of mass 200 g is kept at the top of a frictionless incline which is 10 m long and 3⋅2 m high. How much work was required (a) to lift the block from the ground and put it an the top, (b) to slide the block up the incline? What will be the speed of the block when it reaches the ground if (c) it falls off the incline and drops vertically to the ground (d) it slides down the incline? Take g = 10 m/s2.
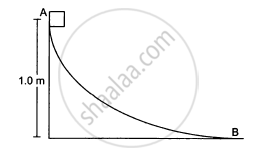
A block weighing 10 N travels down a smooth curved track AB joined to a rough horizontal surface (In the following figure). The rough surface has a friction coefficient of 0⋅20 with the block. If the block starts slipping on the track from a point 1⋅0 m above the horizontal surface, how far will it move on the rough surface?
A block of mass 5 kg is suspended from the end of a vertical spring which is stretched by 10 cm under the load of the block. The block is given a sharp impulse from below, so that it acquires an upward speed of 2 m/s. How high will it rise? Take g = 10 m/s2.
A block of mass 250 g is kept on a vertical spring of spring constant 100 N/m fixed from below. The spring is now compressed 10 cm shorter than its natural length and the system is released from this position. How high does the block rise ? Take g = 10 m/s2.
The bob of a pendulum at rest is given a sharp hit to impart a horizontal velocity \[\sqrt{10 \text{ gl }}\], where l is the length of the pendulum. Find the tension in the string when (a) the string is horizontal, (b) the bob is at its highest point and (c) the string makes an angle of 60° with the upward vertical.
A particle slides on the surface of a fixed smooth sphere starting from the topmost point. Find the angle rotated by the radius through the particle, when it leaves contact with the sphere.
Give example of a situation in which an applied force does not result in a change in kinetic energy.
A rocket accelerates straight up by ejecting gas downwards. In a small time interval ∆t, it ejects a gas of mass ∆m at a relative speed u. Calculate KE of the entire system at t + ∆t and t and show that the device that ejects gas does work = `(1/2)∆m u^2` in this time interval (neglect gravity).
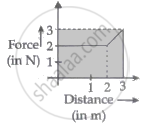
A particle moves in one dimension from rest under the influence of a force that varies with the distance travelled by the particle as shown in the figure. The kinetic energy of the particle after it has travelled 3 m is ______.