Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A particle slides on the surface of a fixed smooth sphere starting from the topmost point. Find the angle rotated by the radius through the particle, when it leaves contact with the sphere.
उत्तर
Let the velocity be \[\nu\] when the body leaves the surface.

From the free-body diagram,
\[\frac{\text{m}\nu^2}{\text{R}} = \text{mg} \cos \theta\]
\[ [\text{ normal reaction }]\]
\[ \nu^2 = \text{Rg} \cos \theta . . . (\text{i})\]
Again, from the work-energy principle,
Change in K.E. = Work done
\[\Rightarrow \frac{1}{2}\text{m}\nu^2 - 0 = \text{mg} \left( \text{R - R} \cos \theta \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \nu^2 = 2\text{ gR} \left( 1 - \cos \theta \right) . . . . (ii)\]
From (i) and (ii),
\[\cos \theta = \frac{2}{3}\]
\[\theta = \cos^{- 1} \left( \frac{2}{3} \right)\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
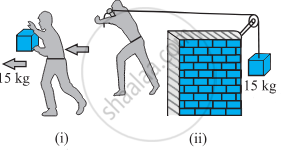
In Figure (i) the man walks 2 m carrying a mass of 15 kg on his hands. In Figure (ii), he walks the same distance pulling the rope behind him. The rope goes over a pulley, and a mass of 15 kg hangs at its other end. In which case is the work done greater?
Is work-energy theorem valid in non-inertial frames?
A ball is given a speed v on a rough horizontal surface. The ball travels through a distance l on the surface and stops. What is the work done by the kinetic friction?
The US athlete Florence Griffith-Joyner won the 100 m sprint gold medal at Seoul Olympics in 1988, setting a new Olympic record of 10⋅54 s. Assume that she achieved her maximum speed in a very short time and then ran the race with that speed till she crossed the line. Take her mass to be 50 kg. Assuming that the track, wind etc. offered an average resistance of one-tenth of her weight, calculate the work done by the resistance during the run.
The US athlete Florence Griffith-Joyner won the 100 m sprint gold medal at Seoul Olympics in 1988, setting a new Olympic record of 10⋅54 s. Assume that she achieved her maximum speed in a very short time and then ran the race with that speed till she crossed the line. Take her mass to be 50 kg. What power Griffith-Joyner had to exert to maintain uniform speed?
A water pump lifts water from 10 m below the ground. Water is pumped at a rate of 30 kg/minute with negligible velocity. Calculate the minimum horsepower that the engine should have to do this.
An unruly demonstrator lifts a stone of mass 200 g from the ground and throws it at his opponent. At the time of projection, the stone is 150 cm above the ground and has a speed of 3 m/s. Calculate the work done by the demonstrator during the process. If it takes one second for the demonstrator to lift the stone and throw it, what horsepower does he use?
In a factory, 2000 kg of metal needs to be lifted by an engine through a distance of 12 m in 1 minute. Find the minimum horsepower of the engine to be used.
A scooter company gives the following specifications about its product:
Weight of the scooter − 95 kg
Maximum speed − 60 km/h
Maximum engine power − 3⋅5 hp
Pick up time to get the maximum speed − 5 s
Check the validity of these specifications.
A block of mass 100 g is moved with a speed of 5⋅0 m/s at the highest point in a closed circular tube of radius 10 cm kept in a vertical plane. The cross-section of the tube is such that the block just fits in it. The block makes several oscillations inside the tube and finally stops at the lowest point. Find the work done by the tube on the block during the process.
A block of mass 250 g is kept on a vertical spring of spring constant 100 N/m fixed from below. The spring is now compressed 10 cm shorter than its natural length and the system is released from this position. How high does the block rise ? Take g = 10 m/s2.
The bob of a pendulum at rest is given a sharp hit to impart a horizontal velocity \[\sqrt{10 \text{ gl }}\], where l is the length of the pendulum. Find the tension in the string when (a) the string is horizontal, (b) the bob is at its highest point and (c) the string makes an angle of 60° with the upward vertical.
A simple pendulum consists of a 50 cm long string connected to a 100 g ball. The ball is pulled aside so that the string makes an angle of 37° with the vertical and is then released. Find the tension in the string when the bob is at its lowest position.
A heavy particle is suspended by a 1⋅5 m long string. It is given a horizontal velocity of \[\sqrt{57} \text{m/s}\] (a) Find the angle made by the string with the upward vertical when it becomes slack. (b) Find the speed of the particle at this instant. (c) Find the maximum height reached by the particle over the point of suspension. Take g = 10 m/s2.
A chain of length l and mass m lies on the surface of a smooth sphere of radius R > l with one end tied to the top of the sphere. Suppose the chain is released and slides down the sphere. Find the kinetic energy of the chain, when it has slid through an angle θ.
A bullet of mass m fired at 30° to the horizontal leaves the barrel of the gun with a velocity v. The bullet hits a soft target at a height h above the ground while it is moving downward and emerges out with half the kinetic energy it had before hitting the target.
Which of the following statements are correct in respect of bullet after it emerges out of the target?
- The velocity of the bullet will be reduced to half its initial value.
- The velocity of the bullet will be more than half of its earlier velocity.
- The bullet will continue to move along the same parabolic path.
- The bullet will move in a different parabolic path.
- The bullet will fall vertically downward after hitting the target.
- The internal energy of the particles of the target will increase.
Suppose the average mass of raindrops is 3.0 × 10–5 kg and their average terminal velocity 9 ms–1. Calculate the energy transferred by rain to each square metre of the surface at a place which receives 100 cm of rain in a year.
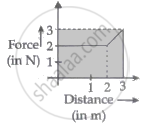
A particle moves in one dimension from rest under the influence of a force that varies with the distance travelled by the particle as shown in the figure. The kinetic energy of the particle after it has travelled 3 m is ______.