Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In a parallelogram ABCD, if `∠`B = 135°, determine the measures of its other angles .
उत्तर
Given `∠`B = 135°
ABCD is a parallelogram
∴`∠`A = `∠`C, `∠`B = `∠`D and `∠`A + `∠`B =180°
`∠`A + `∠`B =180°
`∠`A = 45°
⇒ `∠`A = `∠`C = 45° and `∠`B = `∠`C =135°
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
ABCD is a square. AC and BD intersect at O. State the measure of ∠AOB.
The sides AB and CD of a parallelogram ABCD are bisected at E and F. Prove that EBFD is a parallelogram.
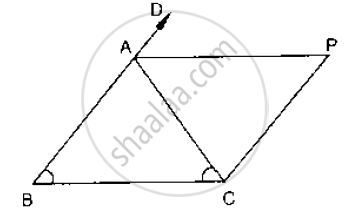
In Fig. below, AB = AC and CP || BA and AP is the bisector of exterior ∠CAD of ΔABC.
Prove that (i) ∠PAC = ∠BCA (ii) ABCP is a parallelogram
In a parallelogram ABCD, if ∠D = 115°, then write the measure of ∠A.
In a parallelogram ABCD, if ∠A = (3x − 20)°, ∠B = (y + 15)°, ∠C = (x + 40)°, then find the values of xand y.
In a parallelogram ABCD, the bisector of ∠A also bisects BC at X. Find AB : AD.
The figure formed by joining the mid-points of the adjacent sides of a rhombus is a
In a quadrilateral ABCD, ∠A + ∠C is 2 times ∠B + ∠D. If ∠A = 140° and ∠D = 60°, then ∠B=
ABCD is a square, diagonals AC and BD meet at O. The number of pairs of congruent triangles with vertex O are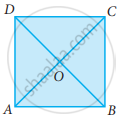
Prove that the quadrilateral formed by the bisectors of the angles of a parallelogram is a rectangle.
