Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In quadrilateral ABCD; angles D = 90°, BC = 38 cm and DC = 25 cm. A circle is inscribed in this quadrilateral which touches AB at point Q such that QB = 27 cm, Find the radius of the circle.
उत्तर
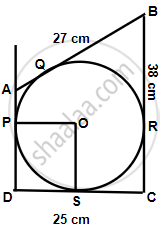
BQ and BR are the tangents from B to the circle.
Therefore, BR = BQ = 27 cm.
Also RC = (38 − 27) = 11 cm
Since CR and CS are the tangents from C to the circle
Therefore, CS = CR = 11 cm
So, DS = (25 − 11) = 14 cm
Now DS and DP are the tangents to the circle
Therefore, DS = DP
Now, `∠`PDS = 90° ...(Given)
And OP ⊥ AD, OS ⊥ DC
Therefore, radius = DS = 14 cm
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The radius of a circle is 8 cm. calculate the length of a tangent draw to this circle from a point at a distance of 10 cm from its centre.
Two circle touch each other externally at point P. Q is a point on the common tangent through P. Prove that the tangents QA and QB are equal.
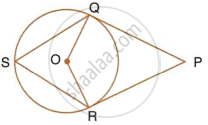
In the following figure, PQ and PR are tangents to the circle, with centre O. If `∠`QPR = 60°, calculate:
- ∠QOR,
- ∠OQR,
- ∠QSR.
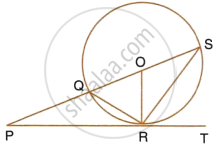
In the given figure, PT touches the circle with centre O at point R. Diameter SQ is produced to meet the tangent TR at P. Given ∠SPR = x° and ∠QRP = y°;
Prove that:
- ∠ORS = y°
- write an expression connecting x and y.
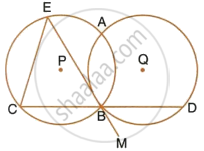
Circles with centres P and Q intersect at points A and B as shown in the figure. CBD is a line segment and EBM is tangent to the circle, with centre Q, at point B. If the circle are congruent; show that CE = BD.
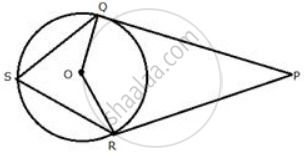
In the following figure, PQ and PR are tangents to the circle, with centre O. If ∠ QPR = 60° , calculate:
∠ OQR
PT is a tangent to the circle at T. If ∠ ABC = 70° and ∠ ACB = 50° ; calculate : ∠ APT
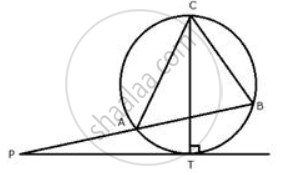
In the figure, PM is a tangent to the circle and PA = AM. Prove that:
(i) Δ PMB is isosceles
(ii) PA x PB = MB2
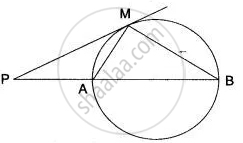
In the Figure, PT is a tangent to a circle. If m(∠BTA) = 45° and m(∠PTB) = 70°. Find m(∠ABT).

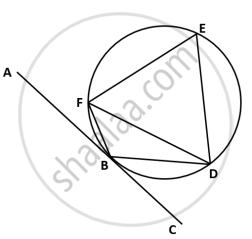
In the given figure, AC is a tangent to circle at point B. ∆EFD is an equilateral triangle and ∠CBD = 40°. Find:
- ∠BFD
- ∠FBD
- ∠ABF
