Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
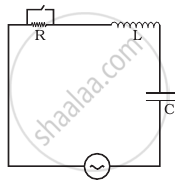
In the LCR circuit shown in figure, the ac driving voltage is v = vm sin ωt.
- Write down the equation of motion for q (t).
- At t = t0, the voltage source stops and R is short circuited. Now write down how much energy is stored in each of L and C.
- Describe subsequent motion of charges.
उत्तर
i. Consider series LCR circuit and tapping key K to short circuit R. Let i be the current in circuit. Then by Kirchhoff's voltage law, when key K is open.
VR+ VL + VC = Vm sin ωt
`iR + L (di(t))/(dt) + (q(t))/C - V_m` sin ωt = 0 .....[∵ i(t) = i = lm sin[ωt + `phi`]
⇒ As charge q(t) changes in circuit with time in AC,
Then `i = (dq(t))/(dt)`
`(di)/(dt) = (d^2q(t))/(dt^2)` .....(Differentiating again)
`R (dq(t))/(dt) + L (d^2q(t))/(dt^2) + (q(t))/C = V_m` sin ωt
`L (d^2q(t))/(dt) + R (dq(t))/(dt) + (q(t))/C = V_m` sin ωt
This is the equation for variation of motion of charge with respect to time.
ii. Let time-dependent charge in circuit is at phase angle with voltage then q = qm cos (ωt + `phi`)
i = `(dq)/(dt) = ω q_m sin (ωt + phi)` ......(I)
`i_m = V_m/Z = V_m/sqrt(R^2 + (X_C - X_L)^2)` ......(II)
`tan phi = (X_C - X_L)/R`
At t = t0, R is short-circuited, then energy stored in L and C, when K is closed will be, `U_L = 1/2 Li` ......(III)
At t = t0
i = im sin (ωt0 + `phi`) ......(IV)
From (II)
`i = V_m/sqrt(R^2 + (X_C - X_L)^2) sin (ωt_0 + phi)` ......(V)
∴ UL = `1/2[V_m/sqrt(R^2 + (X_C - X_L)^2]]^2 sin^2(ωt_0 + phi)`
UC = `q^2/(2C) = 1/(2C) [q_m^2 cos^2 (ωt_0 + pji)]`
Comparing (IV) and (I) Im = qmω
∴ `q_m = i_m/ω`
∴ UC = `1/(2C) * (i_m^2)/ω^2 cos^2 (ωt_0 + phi) = (i_m^2)/(2Cω^2) cos^2 (ωt_0 + phi)`
Using equation (II)
UC = `1/(2Cω^2) [(V_m^2)/(R^2 + (X_C - X_L)^2)]^2 cos^2 (ωt_0 + phi)`
iii. When R is short-circuited, the circuit becomes L-C oscillator. The capacitor will go discharging and all energy will transfer to L and back and forth. Hence there is oscillation of energy from electrostatic to magnetic and vice versa.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A 2 µF capacitor, 100 Ω resistor and 8 H inductor are connected in series with an AC source.
(i) What should be the frequency of the source such that current drawn in the circuit is maximum? What is this frequency called?
(ii) If the peak value of e.m.f. of the source is 200 V, find the maximum current.
(iii) Draw a graph showing variation of amplitude of circuit current with changing frequency of applied voltage in a series LRC circuit for two different values of resistance R1 and R2 (R1 > R2).
(iv) Define the term 'Sharpness of Resonance'. Under what condition, does a circuit become more selective?
Show that the current leads the voltage in phase by π/2 in an AC circuit containing an ideal capacitor ?
The peak voltage of a 220 V AC source is
A bulb rated 60 W at 220 V is connected across a household supply of alternating voltage of 220 V. Calculate the maximum instantaneous current through the filament.
The dielectric strength of air is 3.0 × 106 V/m. A parallel-plate air-capacitor has area 20 cm2 and plate separation 0.10 mm. Find the maximum rms voltage of an AC source that can be safely connected to this capacitor.
An alternating current of 1.5 mA and angular frequency 300 rad/sec flows through a 10 k Ω resistor and a 0.50 µF capacitor in series. Find the rms voltage across the capacitor and impedance of the circuit.
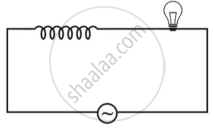
An iron cored coil is connected in series with an electric bulb with an AC source as shown in figure. When iron piece is taken out of the coil, the brightness of the bulb will ______.
A resistor of 50 Ω, a capacitor of `(25/pi)` µF and an inductor of `(4/pi)` H are connected in series across an ac source whose voltage (in volts) is given by V = 70 sin (100 πt). Calculate:
- the net reactance of the circuit
- the impedance of the circuit
- the effective value of current in the circuit.
