Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
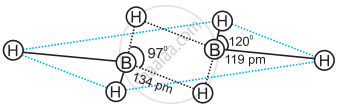
In the structure of diborane ______.
विकल्प
All hydrogen atoms lie in one plane and boron atoms lie in a plane perpendicular to this plane.
2 boron atoms and 4 terminal hydrogen atoms lie in the same plane and 2 bridging hydrogen atoms lie in the perpendicular plane.
4 bridging hydrogen atoms and boron atoms lie in one plane and two terminal hydrogen atoms lie in a plane perpendicular to this plane.
All the atoms are in the same plane.
उत्तर
In the structure of diborane 2 boron atoms and 4 terminal hydrogen atoms lie in the same plane and 2 bridging hydrogen atoms lie in the perpendicular plane.
Explanation:
Four terminal hydrogen atoms and two boron atoms lie in the same plane and two hydrogen atoms forming bridges lie in a plane perpendicular to the rest of the molecule.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Suggest reasons why the B–F bond lengths in BF3 (130 pm) and `"BF"_4^(-)` (143 pm) differ.
How would you explain the lower atomic radius of Ga as compared to Al?
What do you understand by inert pair effect?
Which of the following oxides is acidic in nature?
Ionisation enthalpy (∆iH1kJ mol–1) for the elements of Group 13 follows the order.
Which of the following statements are correct. Answer on the basis of Figure.

(i) The two birdged hydrogen atoms and the two boron atoms lie in one plane;
(ii) Out of six B – H bonds two bonds can be described in terms of 3 centre 2-electron bonds.
(iii) Out of six B – H bonds four B – H bonds can be described in terms of 3 centre 2 electron bonds;
(iv) The four-terminal B – H bonds are two centre-two electron regular bonds.
Aluminium dissolves in mineral acids and aqueous alkalies and thus shows amphoteric character. A piece of aluminium foil is treated with dilute hydrochloric acid or dilute sodium hydroxide solution in a test tube and on bringing a burning matchstick near the mouth of the test tube, a pop sound indicates the evolution of hydrogen gas. The same activity when performed with concentrated nitric acid, reaction doesn’t proceed. Explain the reason.
Match the species given in Column I with the properties mentioned in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) \[\ce{BF^{-}4}\] | (a) Oxidation state of central atom is +4 |
| (ii) AICI3 | (b) Strong oxidising agent |
| (iii) SnO | (c) Lewis acid |
| (iv) PbO2 | (d) Can be further oxidised |
| (e) Tetrahedral shape |
BCl3 exists as monomer whereas AlCl3 is dimerised through halogen bridging. Give reason. Explain the structure of the dimer of AlCl3 also.
Boron fluoride exists as BF3 but boron hydride doesn’t exist as BH3. Give reason. In which form does it exist? Explain its structure.
