Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
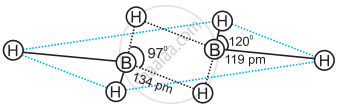
In the structure of diborane ______.
Options
All hydrogen atoms lie in one plane and boron atoms lie in a plane perpendicular to this plane.
2 boron atoms and 4 terminal hydrogen atoms lie in the same plane and 2 bridging hydrogen atoms lie in the perpendicular plane.
4 bridging hydrogen atoms and boron atoms lie in one plane and two terminal hydrogen atoms lie in a plane perpendicular to this plane.
All the atoms are in the same plane.
Solution
In the structure of diborane 2 boron atoms and 4 terminal hydrogen atoms lie in the same plane and 2 bridging hydrogen atoms lie in the perpendicular plane.
Explanation:
Four terminal hydrogen atoms and two boron atoms lie in the same plane and two hydrogen atoms forming bridges lie in a plane perpendicular to the rest of the molecule.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Write a balanced equation for Al + NaOH → ?
The geometry of a complex species can be understood from the knowledge of type of hybridisation of orbitals of central atom. The hybridisation of orbitals of central atom in [Be(OH)4]– and the geometry of the complex are respectively.
The most commonly used reducing agent is ______.
Explain why the following compounds behave as Lewis acids?
BCl3
Aluminium dissolves in mineral acids and aqueous alkalies and thus shows amphoteric character. A piece of aluminium foil is treated with dilute hydrochloric acid or dilute sodium hydroxide solution in a test tube and on bringing a burning matchstick near the mouth of the test tube, a pop sound indicates the evolution of hydrogen gas. The same activity when performed with concentrated nitric acid, reaction doesn’t proceed. Explain the reason.
Explain the following:
Pb4+ acts as an oxidising agent but Sn2+ acts as a reducing agent.
Identify the compounds A, X and Z in the following reactions:
\[\ce{X ->[Δ][370 K] HBO2 ->[Δ][> 370 K] Z}\]
Match the species given in Column I with the hybridisation given in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Boron in [B(OH)4]– | (a) sp2 |
| (ii) Aluminium in [Al(H2O)6]3+ | (b) sp3 |
| (iii) Boron in B2H6 | (c) sp3d2 |
| (iv) Carbon in Buckminsterfullerene | |
| (v) Silicon in \[\ce{SiO^{4-}4}\] | |
| (vi) Germanium in [GeCl6]2– |
Describe the general trends in the following properties of the elements in Groups 13 and 14.
Metallic character
A group 13 element ‘X’ reacts with chlorine gas to produce a compound XCl3. XCl3 is electron deficient and easily reacts with NH3 to form \[\ce{Cl3X –> NH3}\] adduct; however, XCl3 does not dimerize X is ______.
