Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
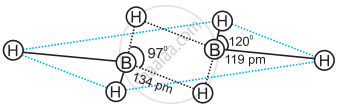
In the structure of diborane ______.
पर्याय
All hydrogen atoms lie in one plane and boron atoms lie in a plane perpendicular to this plane.
2 boron atoms and 4 terminal hydrogen atoms lie in the same plane and 2 bridging hydrogen atoms lie in the perpendicular plane.
4 bridging hydrogen atoms and boron atoms lie in one plane and two terminal hydrogen atoms lie in a plane perpendicular to this plane.
All the atoms are in the same plane.
उत्तर
In the structure of diborane 2 boron atoms and 4 terminal hydrogen atoms lie in the same plane and 2 bridging hydrogen atoms lie in the perpendicular plane.
Explanation:
Four terminal hydrogen atoms and two boron atoms lie in the same plane and two hydrogen atoms forming bridges lie in a plane perpendicular to the rest of the molecule.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What do you understand by inert pair effect?
Write a balanced equation for B2H6 + NH3 → ?
A compound X, of boron reacts with NH3 on heating to give another compound Y which is called inorganic benzene. The compound X can be prepared by treating BF3 with Lithium aluminium hydride. The compounds X and Y are represented by the formulas.
Dry ice is ______.
Explain why the following compounds behave as Lewis acids?
BCl3
When BCl3 is treated with water, it hydrolyses and forms [B[OH]4]– only whereas AlCl3 in acidified aqueous solution forms [Al(H2O)6]3+ ion. Explain what is the hybridisation of boron and aluminium in these species?
Explain the following:
Tl (NO3)3 acts as an oxidising agent.
Describe the general trends in the following properties of the elements in Groups 13 and 14.
Oxidation states
A nonmetallic element of group 13, used in making bullet proof vests is extremely hard solid of black colour. It can exist in many allotropic forms and has unusually high melting point. Its trifluoride acts as Lewis acid towards ammonia. The element exihibits maximum covalency of four. Identify the element and write the reaction of its trifluoride with ammonia. Explain why does the trifluoride act as a Lewis acid.
A group 13 element ‘X’ reacts with chlorine gas to produce a compound XCl3. XCl3 is electron deficient and easily reacts with NH3 to form \[\ce{Cl3X –> NH3}\] adduct; however, XCl3 does not dimerize X is ______.
