Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In Young's double-slit experiment, the two slits are separated by a distance of 1.5 mm, and the screen is placed 1 m away from the plane of the slits. A beam of light consisting of two wavelengths of 650 nm and 520 nm is used to obtain interference fringes.
Find the distance of the third bright fringe for λ = 520 nm on the screen from the central maximum.
उत्तर
Third bright fringe for λ1 = 520 nm is given by
`"x"_3 = (3lamda"D")/"d" = (3 xx 520 xx 10^-9 xx 1)/(1.5 xx 10^-3) = 1.04 xx 10^-3"m"`
= 1.04 mm.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A beam of light consisting of two wavelengths, 650 nm and 520 nm, is used to obtain interference fringes in a Young’s double-slit experiment.
What is the least distance from the central maximum where the bright fringes due to both the wavelengths coincide?
Can we perform Young's double slit experiment with sound waves? To get a reasonable "fringe pattern", what should be the order of separation between the slits? How can the bright fringes and the dark fringes be detected in this case?
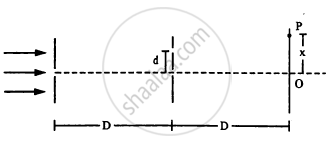
Consider the arrangement shown in the figure. The distance D is large compared to the separation d between the slits.
- Find the minimum value of d so that there is a dark fringe at O.
- Suppose d has this value. Find the distance x at which the next bright fringe is formed.
- Find the fringe-width.
What should be the path difference between two waves reaching a point for obtaining constructive interference in Young’s Double Slit experiment ?
"If the slits in Young's double slit experiment are identical, then intensity at any point on the screen may vary between zero and four times to the intensity due to single slit".
Justify the above statement through a relevant mathematical expression.
In a Young’s double slit experiment, the path difference at a certain point on the screen between two interfering waves is `1/8`th of the wavelength. The ratio of intensity at this point to that at the centre of a bright fringe is close to ______.
A beam of light consisting of two wavelengths 600 nm and 500 nm is used in Young's double slit experiment. The silt separation is 1.0 mm and the screen is kept 0.60 m away from the plane of the slits. Calculate:
- the distance of the second bright fringe from the central maximum for wavelength 500 nm, and
- the least distance from the central maximum where the bright fringes due to both wavelengths coincide.
A fringe width of 6 mm was produced for two slits separated by 1 mm apart. The screen is placed 10 m away. The wavelength of light used is 'x' nm. The value of 'x' to the nearest integer is ______.
Monochromatic green light of wavelength 5 × 10-7 m illuminates a pair of slits 1 mm apart. The separation of bright lines in the interference pattern formed on a screen 2 m away is ______.
In Young's double-slit experiment, the separation between the two slits is d and the distance of the screen from the slits is 1000 d. If the first minima fall at a distance d from the central maximum, obtain the relation between d and λ.
