Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Can we perform Young's double slit experiment with sound waves? To get a reasonable "fringe pattern", what should be the order of separation between the slits? How can the bright fringes and the dark fringes be detected in this case?
उत्तर
Young's double slit experiment can be performed with sound waves, as the sound waves also show interference pattern. To get a reasonable "fringe pattern", the separation of the slits should be of the order of the wavelength of the sound waves used.
In this experiment, the bright and dark fringes can be detected by measuring the intensity of sound using a microphone or any other detector.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The intensity at the central maxima in Young’s double slit experiment is I0. Find out the intensity at a point where the path difference is` lambda/6,lambda/4 and lambda/3.`
A parallel beam of light of wavelength 500 nm falls on a narrow slit and the resulting diffraction pattern is observed on a screen 1 m away. It is observed that the first minimum is a distance of 2.5 mm away from the centre. Find the width of the slit.
Write two characteristics features distinguish the diffractions pattern from the interference fringes obtained in Young’s double slit experiment.
In Young’s double slit experiment using monochromatic light of wavelength λ, the intensity of light at a point on the screen where path difference is λ, is K units. Find out the intensity of light at a point where path difference is λ/3.
How does an unpolarized light incident on a polaroid get polarized? Describe briefly, with the help of a necessary diagram, the polarization of light by reflection from a transparent medium.
Find the angular separation between the consecutive bright fringes in a Young's double slit experiment with blue-green light of wavelength 500 nm. The separation between the slits is \[2 \cdot 0 \times {10}^{- 3}m.\]
In a Young's double slit experiment, using monochromatic light, the fringe pattern shifts by a certain distance on the screen when a mica sheet of refractive index 1.6 and thickness 1.964 micron (1 micron = 10−6 m) is introduced in the path of one of the interfering waves. The mica sheet is then removed and the distance between the screen and the slits is doubled. It is found that the distance between the successive maxima now is the same as the observed fringe-shift upon the introduction of the mica sheet. Calculate the wavelength of the monochromatic light used in the experiment.
Two transparent slabs having equal thickness but different refractive indices µ1 and µ2are pasted side by side to form a composite slab. This slab is placed just after the double slit in a Young's experiment so that the light from one slit goes through one material and the light from the other slit goes through the other material. What should be the minimum thickness of the slab so that there is a minimum at the point P0 which is equidistant from the slits?
The line-width of a bright fringe is sometimes defined as the separation between the points on the two sides of the central line where the intensity falls to half the maximum. Find the line-width of a bright fringe in a Young's double slit experiment in terms of \[\lambda,\] d and D where the symbols have their usual meanings.
Consider the arrangement shown in the figure. By some mechanism, the separation between the slits S3 and S4 can be changed. The intensity is measured at the point P, which is at the common perpendicular bisector of S1S2 and S2S4. When \[z = \frac{D\lambda}{2d},\] the intensity measured at P is I. Find the intensity when z is equal to
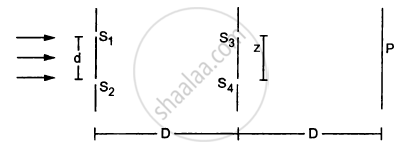
(a) \[\frac{D\lambda}{d}\]
(b) \[\frac{3D\lambda}{2d}\] and
(c) \[\frac{2D\lambda}{d}\]
In Young’s double-slit experiment, using monochromatic light, fringes are obtained on a screen placed at some distance from the slits. If the screen is moved by 5 x 10-2 m towards the slits, the change in the fringe width is 3 x 10-5 m. If the distance between the two slits is 10-3 m, calculate the wavelength of the light used.
When a beam of light is used to determine the position of an object, the maximum accuracy is achieved, if the light is ______.
Two slits in Young's interference experiment have width in the ratio 1 : 2. The ratio of intensity at the maxima and minima in their interference is ______.
Two slits, 4mm apart, are illuminated by light of wavelength 6000 A° what will be the fringe width on a screen placed 2 m from the slits?
In Young's double slit experiment using light of wavelength 600 nm, the slit separation is 0.8 mm and the screen is kept 1.6 m from the plane of the slits. Calculate
- the fringe width
- the distance of (a) third minimum and (b) fifth maximum, from the central maximum.
Monochromatic green light of wavelength 5 × 10-7 m illuminates a pair of slits 1 mm apart. The separation of bright lines in the interference pattern formed on a screen 2 m away is ______.
The central fringe of the interference pattern produced by the light of wavelength 6000 Å is found to shift to the position of the fourth bright fringe after a glass plate of refractive index 1.5 is introduced in the path of one of the beams. The thickness of the glass plate would be ______.
The maximum number of possible interference maxima for slit-separation equal to twice the wavelength in Young's double-slit experiment is ______.
- Assertion (A): In Young's double slit experiment all fringes are of equal width.
- Reason (R): The fringe width depends upon the wavelength of light (λ) used, the distance of the screen from the plane of slits (D) and slits separation (d).
