Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
It is given that ΔABC ~ ΔDFE, ∠A =30°, ∠C = 50°, AB = 5 cm, AC = 8 cm and DF = 7.5 cm. Then, the following is true ______.
विकल्प
DE = 12 cm, ∠F = 50°
DE = 12 cm, ∠F = 100°
EF = 12 cm, ∠D = 100°
EF = 12 cm, ∠D = 30°
उत्तर
It is given that ΔABC ~ ΔDFE, ∠A =30°, ∠C = 50°, AB = 5 cm, AC = 8 cm and DF = 7.5 cm. Then, the following is true DE = 12 cm, ∠F = 100°.
Explanation:
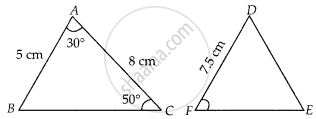
Given, ∆ABC ~ ∆DFE,
Then ∠A = ∠D = 30°,
∠C = ∠E = 50°
∴ ∠B = ∠F = 180° – (30° + 50°) = 100°
Also, AB = 5 cm,
AC = 8 cm
And DF = 7.5 cm
∴ `("AB")/("DF") = ("AC")/("DE")`
`\implies 5/7.5 = 8/("DE")`
∴ DE = `(8 xx 7.5)/5` = 12 cm
Hence, DE = 12 cm, ∠F = 100°
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
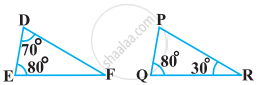
State which pair of triangles in the following figure are similar. Write the similarity criterion used by you for answering the question, and also write the pairs of similar triangles in the symbolic form:
State which pair of triangles in the following figure are similar. Write the similarity criterion used by you for answering the question, and also write the pairs of similar triangles in the symbolic form:
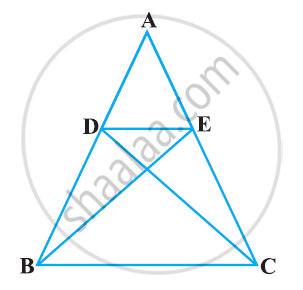
In the following figure, if ΔABE ≅ ΔACD, show that ΔADE ∼ ΔABC.
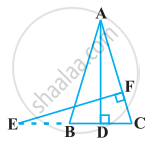
In the following figure, E is a point on side CB produced of an isosceles triangle ABC with AB = AC. If AD ⊥ BC and EF ⊥ AC, prove that ΔABD ∼ ΔECF.
Two triangles ABC and PQR are such that AB = 3 cm, AC = 6cm, ∠𝐴 = 70°, PR = 9cm ∠𝑃 = 70° and PQ = 4.5 cm. Show that ΔABC ∼ΔPQR and state that similarity criterion.
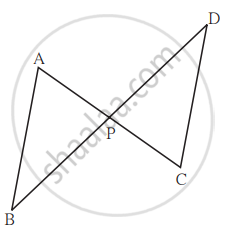
In the given figure, seg AC and seg BD intersect each other in point P and `"AP"/"CP" = "BP"/"DP"`. Prove that, ∆ABP ~ ∆CDP.
In ABC, DE || AB. If CD = 3 cm, EC = 4 cm, BE = 6 cm, then DA is equal to ______.
In figure, two line segments AC and BD intersect each other at the point P such that PA = 6 cm, PB = 3 cm, PC = 2.5 cm, PD = 5 cm, ∠APB = 50° and ∠CDP = 30°. Then, ∠PBA is equal to ______.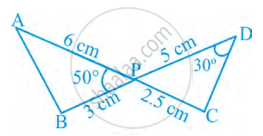
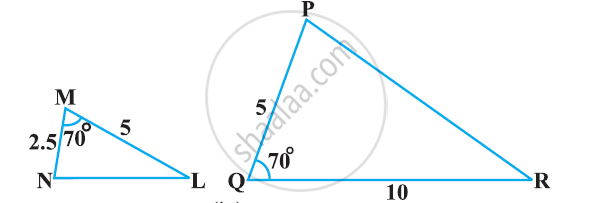
In the given figure, ΔLMN is similar to ΔPQR. To find the measure of ∠N, complete the following activity.
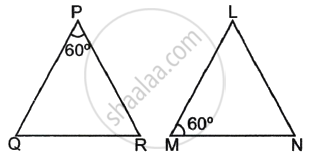
Given: ΔLMN ∼ ΔPQR
Since ΔLMN ∼ ΔPQR, therefore, corresponding angles are equal.
So, ∠L ≅ `square`
⇒ ∠L = `square`
We know, the sum of angles of a triangle = `square`
∴ ∠L + ∠M + ∠N = `square`
Substituting the values of ∠L and ∠M in equation (i),
`square` + `square` + ∠N = `square`
∠N + `square` = `square`
∠N = `square` – `square`
∠N = `square`
Hence, the measure of ∠N is `square`.
A tangent ADB is drawn to a circle at D whose centre is C. Also, PQ is a chord parallel to AB and ∠QDB = 50°. Find the value of ∠PDQ.

