Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Let X be a discrete random variable with the following p.m.f
`"P"(x) = {{:(0.3, "for" x = 3),(0.2, "for" x = 5),(0.3, "for" x = 8),(0.2, "for" x = 10),(0, "otherwise"):}`
Find and plot the c.d.f. of X.
उत्तर
F(3) = P(x ≤ 3)
= P(3)
= 0.3
F(5) = P(x ≤ 5)
= P(x = 3) + (x = 5)
= 0.3 + 0.2
= 0.5
F(8) = P(x ≤ 8)
= P(3) + P(5) + P(8)
= 0.3 + 0.2 + 0.3
= 0.8
F(10) = P(x ≤ 10)
= P(3) + P(5) + P(8) + P(10)
= 0.3 + 0.2 + 0.3 + 0.2
= 1
`"F"_x(x) = {{:(0, "for" x < 3),("P"_x(3) = 0.3, "for" 3 ≤ x < 5),("P"_x(3) + "P"_x(5) = 0.5, "for" 5 ≤ x < 8),("P"_x(3) + "P"_x(5) + "P"_x(8) = 0.8, "for" 8 ≤ x < 10),(1, "for" x ≥ 10):}`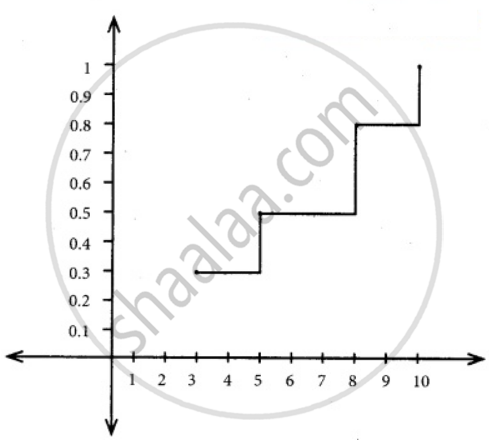
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A continuous random variable X has the following distribution function
F(x) = `{{:(0",", "if" x ≤ 1),("k"(x - 1)^4",", "if" 1 < x ≤ 3),(1",", "if" x > 3):}`
Find the Probability density function
Explain what are the types of random variable?
Define dicrete random Variable
Distinguish between discrete and continuous random variables.
Choose the correct alternative:
A variable that can assume any possible value between two points is called
Choose the correct alternative:
A formula or equation used to represent the probability distribution of a continuous random variable is called
Choose the correct alternative:
In a discrete probability distribution, the sum of all the probabilities is always equal to
Let X be a random variable with a cumulative distribution function.
F(x) = `{{:(0",", "if" x < 0),(x/8",", "if" 0 ≤ x ≤ 1),(1/4 + x/8",", "if" 1 ≤ x ≤ 2),(3/4 + x/12",", "if" 2 ≤ x < 3),(1",", "for" 3 ≤ x):}`
Compute: (i) P(1 ≤ X ≤ 2) and (ii) P(X = 3)
Let X be a random variable with a cumulative distribution function.
F(x) = `{{:(0",", "if" x < 0),(x/8",", "if" 0 ≤ x ≤ 1),(1/4 + x/8",", "if" 1 ≤ x ≤ 2),(3/4 + x/12",", "if" 2 ≤ x < 3),(1",", "for" 3 ≤ x):}`
Is X a discrete random variable? Justify your answer
The p.d.f. of X is defined as
f(x) = `{{:("k"",", "for" 0 < x ≤ 4),(0",", "otherwise"):}`
Find the value of k and also find P(2 ≤ X ≤ 4)
