Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Match structures given in Column I with the type of detergents given in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) \[\ce{CH3(CH2)16COO(CH2CH2O) nCH2CH2OH}\] | (a) Cationic detergent |
| (ii) \[\ce{C17H35COO- Na+}\] | (b) Anionic detergent |
| (iii) \[\ce{CH3-(CH2)10CH2SO3- Na+}\] | (c) Nonionic detergent |
|
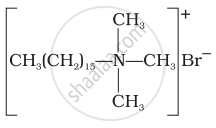
(iv) |
(d) Soap |
उत्तर
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) \[\ce{CH3(CH2)16COO(CH2CH2O) nCH2CH2OH}\] | (c) Nonionic detergent |
| (ii) \[\ce{C17H35COO- Na+}\] | (d) Soap |
| (iii) \[\ce{CH3-(CH2)10CH2SO3- Na+}\] | (b) Anionic detergent |
|
(iv) |
(a) Cationic detergent |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain the following terms with suitable examples - Non-ionic detergents
Label the hydrophilic and hydrophobic parts in the following compounds.
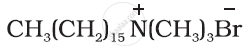
Define the following term with a suitable example in each:
Cationic detergents
Explain why some times foaming is seen in river water near the place where sewage water is poured after treatment?
Hair shampoos belong to which class of synthetic detergent?
Dishwashing soaps are synthetic detergents. What is their chemical nature?
Draw the diagram showing micelle formation by the following detergent.
\[\ce{CH3(CH2)10CH2OS\overset{-}{O}3\overset{+}{N}a}\]
Synthetic detergents have advantage over usual soaps as far as cleansing power is concerned. But use of synthetic detergents over a long time creates environmental pollution. How can the pollution caused by synthetic detergents be minimised? Classify the detergents according to their chemical nature.
Explain the following term with suitable example cationic detergents.
Explain the Following Term with Suitable Examples.
Cationic Detergents