Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Read the following statements below carefully and state, with reasons, if it is true or false
The Young’s modulus of rubber is greater than that of steel;
उत्तर
False
For a given stress, the strain in rubber is more than it is in steel.
Young’s modulus, Y = Stress/Strain
For a constant stress: `Y prop 1/Strain`
Hence, Young’s modulus for rubber is less than it is for steel.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 3.0 × 10–5 m2 stretches by the same amount as a copper wire of length 3.5 m and cross-sectional area of 4.0 × 10–5 m2 under a given load. What is the ratio of Young’s modulus of steel to that of copper?
The stress-strain graphs for materials A and B are shown in Figure
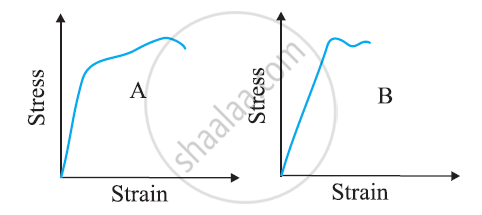
The graphs are drawn to the same scale.
(a) Which of the materials has the greater Young’s modulus?
(b) Which of the two is the stronger material?
Two wires of diameter 0.25 cm, one made of steel and the other made of brass are loaded as shown in Fig. 9.13. The unloaded length of steel wire is 1.5 m and that of brass wire is 1.0 m. Compute the elongations of the steel and the brass wires.

The length of a metal wire is l1 when the tension in it T1 and is l2 when the tension is T2. The natural length of the wire is
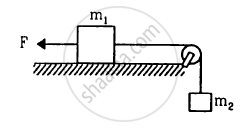
Consider the situation shown in figure. The force F is equal to the m2 g/2. If the area of cross section of the string is A and its Young modulus Y, find the strain developed in it. The string is light and there is no friction anywhere.
A copper wire of cross-sectional area 0.01 cm2 is under a tension of 20N. Find the decrease in the cross-sectional area. Young modulus of copper = 1.1 × 1011 N m−2 and Poisson ratio = 0.32.
`["Hint" : (Delta"A")/"A"=2(Delta"r")/"r"]`
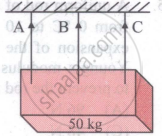
A uniform rectangular block of mass of 50 kg is hung horizontally with the help of three wires A, B and C each of length and area of 2m and 10mm2 respectively as shown in the figure. The central wire is passing through the centre of gravity and is made of material of Young's modulus 7.5 x 1010 Nm−2 and the other two wires A and C symmetrically placed on either side of the wire B are of Young's modulus 1011 Nm−2 The tension in the wires A and B will be in the ratio of:
If the yield strength of steel is 2.5 × 108 Nm–2, what is the maximum weight that can be hung at the lower end of the wire?
A metal wire of length L, area of cross section A and Young's modulus Y behaves as a spring of spring constant k given by:
A uniform metal rod of 2 mm2 cross section is heated from 0°C to 20°C. The coefficient of linear expansion of the rod is 12 × 10-6/°C, it's Young's modulus is 1011 N/m2. The energy stored per unit volume of the rod is ______.
