Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Represent graphically a displacement of 40 km, 30° east of north.
उत्तर
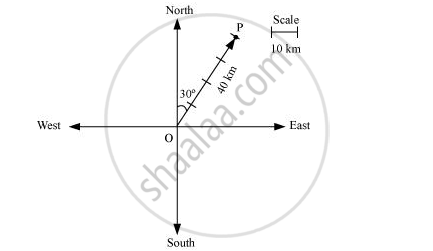
Here, vector `bar(OP)` represents the displacement of 40 km, 30° East of North.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Find the direction ratios of a vector perpendicular to the two lines whose direction ratios are -2, 1, -1, and -3, -4, 1.
If `bara, barb, bar c` are the position vectors of the points A, B, C respectively and ` 2bara + 3barb - 5barc = 0` , then find the ratio in which the point C divides line segment AB.
If `bara, barb, barc` are position vectors of the points A, B, C respectively such that `3bara+ 5barb-8barc = 0`, find the ratio in which A divides BC.
Classify the following as scalar and vector quantity.
Time period
In Figure, identify the following vector.

Coinitial
Two vectors having the same magnitude are collinear.
Find the direction cosines of the vector `hati + 2hatj + 3hatk`.
Find the direction cosines of the vector joining the points A (1, 2, -3) and B (-1, -2, 1) directed from A to B.
Find the position vector of the mid point of the vector joining the points P (2, 3, 4) and Q (4, 1, – 2).
Show that the points A, B and C with position vectors `veca = 3hati - 4hatj - 4hatk`, `vecb = 2hati - hatj + hatk` and `vecc = hati - 3hatj - 5hatk`, respectively form the vertices of a right angled triangle.
Write down a unit vector in XY-plane, making an angle of 30° with the positive direction of the x-axis.
Express \[\vec{AB}\] in terms of unit vectors \[\hat{i}\] and \[\hat{j}\], when the points are A (4, −1), B (1, 3)
Find \[\left| \vec{A} B \right|\] in each case.
ABCD is a parallelogram. If the coordinates of A, B, C are (−2, −1), (3, 0) and (1, −2) respectively, find the coordinates of D.
Dot product of a vector with \[\hat{i} + \hat{j} - 3\hat{k} , \hat{i} + 3\hat{j} - 2 \hat{k} \text{ and } 2 \hat{i} + \hat{j} + 4 \hat{k}\] are 0, 5 and 8 respectively. Find the vector.
The adjacent sides of a parallelogram are represented by the vectors \[\vec{a} = \hat{i} + \hat{j} - \hat{k}\text{ and }\vec{b} = - 2 \hat{i} + \hat{j} + 2 \hat{k} .\]
Find unit vectors parallel to the diagonals of the parallelogram.
Dot products of a vector with vectors \[\hat{i} - \hat{j} + \hat{k} , 2\hat{ i} + \hat{j} - 3\hat{k} \text{ and } \text{i} + \hat{j} + \hat{k}\] are respectively 4, 0 and 2. Find the vector.
Show that the vectors \[\vec{a} = \frac{1}{7}\left( 2 \hat{i} + 3 \hat{j} + 6 \hat{k} \right), \vec{b} = \frac{1}{7}\left( 3\hat{i} - 6 {j} + 2 \hat{k} \right), \vec{c} = \frac{1}{7}\left( 6 \hat{i} + 2 \hat{j} - 3 {k} \right)\] are mutually perpendicular unit vectors.
If \[\vec{a} = 2 \hat{i} - \hat{j} + \hat{k}\] \[\vec{b} = \hat{i} + \hat{j} - 2 \hat{k}\] \[\vec{c} = \hat{i} + 3 \hat{j} - \hat{k}\] find λ such that \[\vec{a}\] is perpendicular to \[\lambda \vec{b} + \vec{c}\]
If \[\vec{\alpha} = 3 \hat{i} + 4 \hat{j} + 5 \hat{k} \text{ and } \vec{\beta} = 2 \hat{i} + \hat{j} - 4 \hat{k} ,\] then express \[\vec{\beta}\] in the form of \[\vec{\beta} = \vec{\beta_1} + \vec{\beta_2} ,\] where \[\vec{\beta_1}\] is parallel to \[\vec{\alpha} \text{ and } \vec{\beta_2}\] is perpendicular to \[\vec{\alpha}\]
If either \[\vec{a} = \vec{0} \text{ or } \vec{b} = \vec{0}\] then \[\vec{a} \cdot \vec{b} = 0 .\] But the converse need not be true. Justify your answer with an example.
Show that the vectors \[\vec{a} = 3 \hat{i} - 2 \hat{j} + \hat{k} , \vec{b} = \hat{i} - 3 \hat{j} + 5 \hat{k} , \vec{c} = 2 \hat{i} + \hat{j} - 4 \hat{k}\] form a right-angled triangle.
If A, B and C have position vectors (0, 1, 1), (3, 1, 5) and (0, 3, 3) respectively, show that ∆ ABC is right-angled at C.
Find the vector from the origin O to the centroid of the triangle whose vertices are (1, −1, 2), (2, 1, 3) and (−1, 2, −1).
Find the unit vector in the direction of vector \[\overrightarrow{PQ} ,\]
where P and Q are the points (1, 2, 3) and (4, 5, 6).
Show that the points \[A \left( 2 \hat{i} - \hat{j} + \hat{k} \right), B \left( \hat{i} - 3 \hat{j} - 5 \hat{k} \right), C \left( 3 \hat{i} - 4 \hat{j} - 4 \hat{k} \right)\] are the vertices of a right angled triangle.
Find the value of x for which \[x \left( \hat{i} + \hat{j} + \hat{k} \right)\] is a unit vector.
If \[\vec{a} = \hat{i} + \hat{j} + \hat{k} , \vec{b} = 2 \hat{i} - \hat{j} + 3 \hat{k} \text{ and }\vec{c} = \hat{i} - 2 \hat{j} + \hat{k} ,\] find a unit vector parallel to \[2 \vec{a} - \vec{b} + 3 \vec{c .}\]
If \[\overrightarrow{AO} + \overrightarrow{OB} = \overrightarrow{BO} + \overrightarrow{OC} ,\] prove that A, B, C are collinear points.
Show that the vectors \[2 \hat{i} - 3 \hat{j} + 4 \hat{k}\text{ and }- 4 \hat{i} + 6 \hat{j} - 8 \hat{k}\] are collinear.
If A, B, C, D are the points with position vectors `hat"i" + hat"j" - hat"k", 2hat"i" - hat"j" + 3hat"k", 2hat"i" - 3hat"k", 3hat"i" - 2hat"j" + hat"k"`, respectively, find the projection of `vec"AB"` along `vec"CD"`.
Position vector of a point P is a vector whose initial point is origin.
The unit normal to the plane 2x + y + 2z = 6 can be expressed in the vector form as
Let (h, k) be a fixed point where h > 0, k > 0. A straight line passing through this point cuts the positive direction of the coordinate axes at the points P and Q. Then the minimum area of the ΔOPQ. O being the origin, is
Area of rectangle having vertices A, B, C and D will position vector `(- hati + 1/2hatj + 4hatk), (hati + 1/2hatj + 4hatk) (hati - 1/2hatj + 4hatk)` and `(-hati - 1/2hatj + 4hatk)` is
Assertion (A): If a line makes angles α, β, γ with positive direction of the coordinate axes, then sin2 α + sin2 β + sin2 γ = 2.
Reason (R): The sum of squares of the direction cosines of a line is 1.
Find the position vector of a point R which divides the line joining two points P and Q whose position vectors are `hati + 2hatj - hatk` and `-hati + hatj + hatk` respectively, internally the ratio 2:1.
