Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Represent graphically a displacement of 40 km, 30° east of north.
Solution
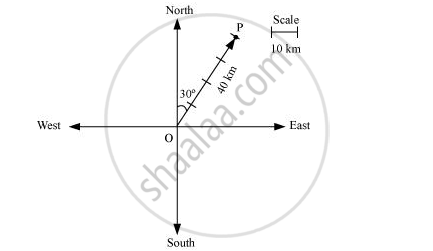
Here, vector `bar(OP)` represents the displacement of 40 km, 30° East of North.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Find the direction ratios of a vector perpendicular to the two lines whose direction ratios are -2, 1, -1, and -3, -4, 1.
Write the position vector of the point which divides the join of points with position vectors `3veca-2vecb and 2veca+3vecb` in the ratio 2 : 1.
Find the position vector of a point which divides the join of points with position vectors `veca-2vecb" and "2veca+vecb`externally in the ratio 2 : 1
Find the value of 'p' for which the vectors `3hati+2hatj+9hatk and hati-2phatj+3hatk` are parallel
If `bara, barb, barc` are position vectors of the points A, B, C respectively such that `3bara+ 5barb-8barc = 0`, find the ratio in which A divides BC.
Classify the following measures as scalar and vector.
10 kg
In Figure, identify the following vector.

Coinitial
Find the direction cosines of the vector `hati + 2hatj + 3hatk`.
Find the position vector of a point R which divides the line joining two points P and Q whose position vectors are `hati + 2hatj - hatk` and `-hati + hatj + hatk` respectively, externally in the ratio 2:1.
If θ is the angle between two vectors `veca` and `vecb`, then `veca . vecb >= 0` only when ______.
Express \[\vec{AB}\] in terms of unit vectors \[\hat{i}\] and \[\hat{j}\], when the points are A (4, −1), B (1, 3)
Find \[\left| \vec{A} B \right|\] in each case.
ABCD is a parallelogram. If the coordinates of A, B, C are (−2, −1), (3, 0) and (1, −2) respectively, find the coordinates of D.
Find the angle between the vectors \[\vec{a} \text{ and } \vec{b}\] where \[\vec{a} = \hat{i} - \hat{j} \text{ and } \vec{b} = \hat{j} + \hat{k}\]
Find the angle between the vectors \[\vec{a} \text{ and } \vec{b}\] \[\vec{a} = 2\hat{i} - \hat{j} + 2\hat{k} \text{ and } \vec{b} = 4\hat{i} + 4 \hat{j} - 2\hat{k}\]
Find a unit vector parallel to the vector \[\hat{i} + \sqrt{3} \hat{j}\]
Find the angle between the vectors \[\vec{a} = \hat{i} + 2 \hat{j} - \hat{k} , \vec{b} = \hat{i} - \hat{j} + \hat{k}\]
If \[\hat{a} \text{ and } \hat{b}\] are unit vectors inclined at an angle θ, prove that \[\cos\frac{\theta}{2} = \frac{1}{2}\left| \hat{a} + \hat{b} \right|\]
If \[\hat{ a } \text{ and } \hat{b }\] are unit vectors inclined at an angle θ, prove that
\[\tan\frac{\theta}{2} = \frac{\left| \hat{a} -\hat{b} \right|}{\left| \hat{a} + \hat{b} \right|}\]
If \[\vec{a} = 2 \hat{i} - \hat{j} + \hat{k}\] \[\vec{b} = \hat{i} + \hat{j} - 2 \hat{k}\] \[\vec{c} = \hat{i} + 3 \hat{j} - \hat{k}\] find λ such that \[\vec{a}\] is perpendicular to \[\lambda \vec{b} + \vec{c}\]
If \[\vec{p} = 5 \hat{i} + \lambda \hat{j} - 3 \hat{k} \text{ and } \vec{q} = \hat{i} + 3 \hat{j} - 5 \hat{k} ,\] then find the value of λ, so that \[\vec{p} + \vec{q}\] and \[\vec{p} - \vec{q}\] are perpendicular vectors.
If either \[\vec{a} = \vec{0} \text{ or } \vec{b} = \vec{0}\] then \[\vec{a} \cdot \vec{b} = 0 .\] But the converse need not be true. Justify your answer with an example.
If \[\vec{a} = 2 \hat{i} + 2 \hat{j} + 3 \hat{k} , \vec{b} = - \hat{i} + 2 \hat{j} + \hat{k} \text{ and } \vec{c} = 3 \hat{i} + \hat{j}\] \[\vec{a} + \lambda \vec{b}\] is perpendicular to \[\vec{c}\] then find the value of λ.
Find the angles of a triangle whose vertices are A (0, −1, −2), B (3, 1, 4) and C (5, 7, 1).
Show that the points whose position vectors are \[\vec{a} = 4 \hat{i} - 3 \hat{j} + \hat{k} , \vec{b} = 2 \hat{i} - 4 \hat{j} + 5 \hat{k} , \vec{c} = \hat{i} - \hat{j}\] form a right triangle.
Find the value of x for which \[x \left( \hat{i} + \hat{j} + \hat{k} \right)\] is a unit vector.
If \[\overrightarrow{AO} + \overrightarrow{OB} = \overrightarrow{BO} + \overrightarrow{OC} ,\] prove that A, B, C are collinear points.
If \[\vec{a} \times \vec{b} = \vec{c} \times \vec{d} \text { and } \vec{a} \times \vec{c} = \vec{b} \times \vec{d}\] , show that \[\vec{a} - \vec{d}\] is parallel to \[\vec{b} - \vec{c}\] where \[\vec{a} \neq \vec{d} \text { and } \vec{b} \neq \vec{c}\] .
if `hat"i" + hat"j" + hat"k", 2hat"i" + 5hat"j", 3hat"i" + 2 hat"j" - 3hat"k" and hat"i" - 6hat"j" - hat"k"` respectively are the position vectors A, B, C and D, then find the angle between the straight lines AB and CD. Find whether `vec"AB" and vec"CD"` are collinear or not.
If `vec"a"` and `vec"b"` are the position vectors of A and B, respectively, find the position vector of a point C in BA produced such that BC = 1.5 BA.
A vector `vec"r"` has magnitude 14 and direction ratios 2, 3, – 6. Find the direction cosines and components of `vec"r"`, given that `vec"r"` makes an acute angle with x-axis.
If A, B, C, D are the points with position vectors `hat"i" + hat"j" - hat"k", 2hat"i" - hat"j" + 3hat"k", 2hat"i" - 3hat"k", 3hat"i" - 2hat"j" + hat"k"`, respectively, find the projection of `vec"AB"` along `vec"CD"`.
Position vector of a point P is a vector whose initial point is origin.
The unit normal to the plane 2x + y + 2z = 6 can be expressed in the vector form as
Let (h, k) be a fixed point where h > 0, k > 0. A straight line passing through this point cuts the positive direction of the coordinate axes at the points P and Q. Then the minimum area of the ΔOPQ. O being the origin, is
If `veca, vecb, vecc` are vectors such that `[veca, vecb, vecc]` = 4, then `[veca xx vecb, vecb xx vecc, vecc xx veca]` =
Find the direction ratio and direction cosines of a line parallel to the line whose equations are 6x − 12 = 3y + 9 = 2z − 2
A line l passes through point (– 1, 3, – 2) and is perpendicular to both the lines `x/1 = y/2 = z/3` and `(x + 2)/-3 = (y - 1)/2 = (z + 1)/5`. Find the vector equation of the line l. Hence, obtain its distance from the origin.
