Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Show that the child’s new kinetic energy of rotation is more than the initial kinetic energy of rotation. How do you account for this increase in kinetic energy?
उत्तर
`"Final Kinetic Energy of rotation"/"Initial Kinetic Energy of rotation" = (1/2 I_2omega_2^2)/(1/2I_1omega_1^2) = (1/2 I_2(2piv_2)^2)/(1/2I_1(2piv_1)^2) = (I_2v_2^2)/(I_1v_1^2) = (2/5I_1xx(100)^2)/(2/5I_1xx(40)^2) = 2.5`
Clearly, final (K.E) becomes more because the child used his internal energy when he folds his hands to increase the kinetic energy
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Torques of equal magnitude are applied to a hollow cylinder and a solid sphere, both having the same mass and radius. The cylinder is free to rotate about its standard axis of symmetry, and the sphere is free to rotate about an axis passing through its centre. Which of the two will acquire a greater angular speed after a given time?
A hoop of radius 2 m weighs 100 kg. It rolls along a horizontal floor so that its centre of mass has a speed of 20 cm/s. How much work has to be done to stop it?
The moment of inertia of a uniform semicircular wire of mass M and radius r about a line perpendicular to the plane of the wire through the centre is ___________ .
A diver having a moment of inertia of 6⋅0 kg-m2 about an axis thorough its centre of mass rotates at an angular speed of 2 rad/s about this axis. If he folds his hands and feet to decrease the moment of inertia to 5⋅0 kg-m2, what will be the new angular speed?
A boy is seated in a revolving chair revolving at an angular speed of 120 revolutions per minute. Two heavy balls form part of the revolving system and the boy can pull the balls closer to himself or may push them apart. If by pulling the balls closer, the boy decreases the moment of inertia of the system from 6 kg-m2 to 2 kg-m2, what will be the new angular speed?
A wheel of moment of inertia 0⋅10 kg-m2 is rotating about a shaft at an angular speed of 160 rev/minute. A second wheel is set into rotation at 300 rev/minute and is coupled to the same shaft so that both the wheels finally rotate with a common angular speed of 200 rev/minute. Find the moment of inertia of the second wheel.
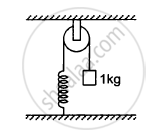
The pulley shown in the following figure has a radius of 20 cm and moment of inertia 0⋅2 kg-m2. The string going over it is attached at one end to a vertical spring of spring constant 50 N/m fixed from below, and supports a 1 kg mass at the other end. The system is released from rest with the spring at its natural length. Find the speed of the block when it has descended through 10 cm. Take g = 10 m/s2.
A wheel of mass 15 kg has a moment of inertia of 200 kg-m2 about its own axis, the radius of gyration will be:
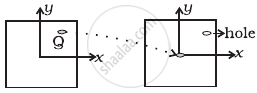
A uniform square plate has a small piece Q of an irregular shape removed and glued to the centre of the plate leaving a hole behind (Figure). The moment of inertia about the z-axis is then ______.
Moment of inertia (M.I.) of four bodies, having same mass and radius, are reported as :
I1 = M.I. of thin circular ring about its diameter,
I2 = M.I. of circular disc about an axis perpendicular to disc and going through the centre,
I3 = M.I. of solid cylinder about its axis and
I4 = M.I. of solid sphere about its diameter.
Then -
