Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Stainless steel is an alloy of _______.
विकल्प
copper
tin
zinc
iron
उत्तर
Stainless steel is an alloy of iron.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Give two examples of alloys with their chemical composition.
Explain the terms Corrosion
Two methods by which rusting of iron can be prevented are ______ and ______.
Explain why rusting of iron objects is faster in coastal areas than in deserts.
Explain why Iron sheets are coated with zinc during galvanization.
Name any three objects (or structures) which are gradually damaged by the corrosion of iron and steel.
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
The corrosion of copper produces a .............. coating of basic copper carbonate on its surface
Why is an iron grill painted frequently?
What is the corrosion of iron known as?
Name five methods of preventing rusting of iron.
Four metals P, Q, R and S are all obtained by the reduction of their oxides with carbon. Metal P is used to form a thin layer over the sheets of metal S to prevent its corrosion. Metal Q is used for electroplating tiffin boxes made of metal S whereas metal R is used in making car batteries. Metals Q and R form an alloy called solder. What are metals P, Q, R and S? How have you arrived at this conclusion?
What is corrosion? What are necessary conditions for corrosion?
Compare roasting and calcination.
Complete the process of iron rusting by filling the blanks. Suggest a way to prohibit the process.
The iron rust is formed due to........................... reaction. Different
regions on iron surface become anode and cathode.
Reaction on anode region :
`F_e(s) → Fe^(2+) (aq) +2e^-`
Reaction on anode region :
`O_2(g) + 4H^+(aq) +............................ → 2H_2 O (l) `
When Fe2+ ions migrate from anode region they react with ................... to form Fe3+ ions.
A reddish coloured hydrated oxide is formed from ............... ions. It is called rust.
`2Fe_(3+) (aq) + 4H_2O(l) → ................. + 6H_+(aq) `
A way to prevent rusting ..................................................................
Identify the process shown in the diagram and explain it in short
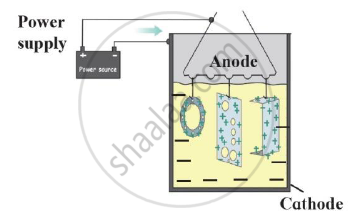
What are the adverse effects of corrosion?
Give reason.
An iron article should be given a coat of paint
Give a reason why rust turns moist red litmus blue.
State whether the statement given below is true or false. If false write the correct statement.
Graphite is a lustrous non-metal which conducts electricity.
Write a short note on Alloying.
Which of the following method is used to prevent the accumulation of greenish layer on brass due to corrosion?
Corrosion of silver causes a black layer of _______.
_______ forms a green colour in the water.
When one of the metals in an alloy is mercury the alloy is called _______.
Find the odd one out and give its explanation.
What is rust?
Observe the following diagram and give answers.
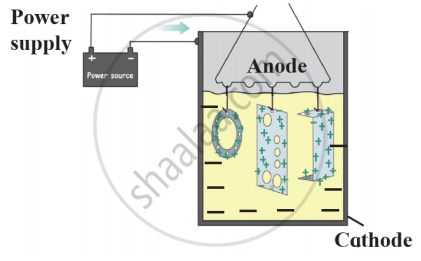
- Name this method of prevention of corrosion.
- For prevention of which metal this method is used?
- What is used as anode in this method?
The process of coating the surface of the metal with a thin layer of zinc is called ______
What is rust?
Amalgam is an alloy of ____________.
The diagram shows the reaction between metal and dil. acid.
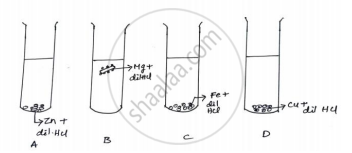
What is the reason for different behaviour of Mg in test tube B?
The table shown below gives information about four substances: A, B, C and D.
| SUBSTANCE | MELTING POINT (K) | ELECTRICAL CONDUCTIVITY | |
| SOLID | LIQUID/ AQUEOUS | ||
| A | 295 | Good | Good |
| B | 1210 | Poor | Good |
| C | 1890 | Poor | Good |
| D | 1160 | Poor | Poor |
Identify Ionic compounds from the above given substances.
The iron pillar near the Qutub Minar in Delhi is famous for the following facts. Which of these facts is responsible for its long stability?
State whether the following statements are true or false:
Ships suffer a lot of damage though they are painted.
In ______ process a layer of molten tin is deposited on metals.
