Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The CGS unit of G is dyne.cm2/g2.
विकल्प
Right
Wrong
उत्तर
The CGS unit of G is dyne.cm2/g2 - Right
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State whether the following statement is true or false :
The value of G on the moon is about one-sixth `(1/6)`of the value of G on the earth.
Fill in the following blank with suitable word :
The value of g on the earth is about………………. of that on the moon.
Is the acceleration due to gravity of earth ‘g’ a constant ? Discuss.
The value of g is highest at the equator.
The value of G varies from place to place.
Write scientific reason.
The value of acceleration g is greater at the pole than at the equator.
Write scientific reason.
The weight of an object varies on different planets.
When the value of acceleration due to gravity 'g' becomes `(g/3)` above the earth's surface at height 'h' then relation between 'h' and 'R' is ______.
R =radius of the earth
The force of attraction between two unit point masses separated by a unit distance is called
On the earth, a stone is thrown from a height in a direction parallel to the earth’s surface while another stone is simultaneously dropped from the same height. Which stone would reach the ground first and why?
Suppose the gravity of the earth suddenly becomes zero, then in which direction will the moon begin to move if no other celestial body affects it?
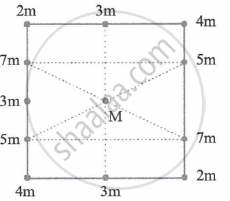
A central particle M is surrounded by a square array of other particles, separated by either distanced or distance d/2 along the perimeter o the square. The magnitude of the gravitational force on the central particle due to the other particles is ______.
A mass attached to one end of a string crosses top-most point on a vertical circle with critical speed. Its centripetal acceleration when string becomes horizontal will be ______. (g = gravitational acceleration)
A lift of mass 'm' is connected to a rope which is moving upward with maximum acceleration 'a'. For maximum safe stress, the elastic limit of the rope is 'T'. The minimum diameter of the rope is ______.
(g = gravitational acceleration)
The depth 'd' at which the value of acceleration due to gravity becomes `"I"/"n"` times the value at the earth's surface is ______. (R = radius of earth)
The value of gravitational acceleration g at a height h above the earth's surface is `"g"/4`, then ______. (R = radius of earth)
The difference in the acceleration due to gravity at the pole and equator is ______.
(g = acceleration due to gravity, R = radius of the earth; θ = latitude, ω = angular velocity, cos0° = 1, cos90° = 0)
A uniform ring of mass M and radius r is placed directly above a uniform sphere of mass 8M and of same radius R. The centre of the ring is at a distance of d = `sqrt3`R from the centre of the sphere. The gravitational attraction between the sphere and the ring is ______.
