Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Use a graph sheet for this question, take 2 cm = 1 unit along both x and y-axis:
- Plot the points A (3, 2) and B (5, 0). Reflect point A on the y-axis to A΄. Write co-ordinates of A΄.
- Reflect point B on the line AA΄ to B΄. Write the co-ordinates of B΄.
- Name the closed figure A’B’AB.
उत्तर

(a) A' (- 3, 2)
(b) Since we know that,
The reflection of point (a, b) with respect to line y = k is a point (a, 2k- b)
Here, k = 2, a = 5, b = 0
∴ B' = (5, 2 × 2 - 0)
∴ B' = (5, 4)
(c) A'B'AB is an arrowhead
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
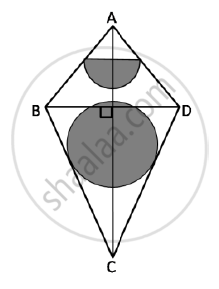
The given figure represents a kite with a circular and a semicircular motifs stuck on it.
The radius of a circle is 2.5 cm and the semicircle is 2 cm. If diagonals AC and BD are
of lengths 12 cm and 8 cm respectively, find the area of the:
1) Shaded part. Give your answer correct to the nearest whole number.
2) Unshaded part
Use graph paper for this question (Take 2 cm = 1 unit along both x and y-axis). ABCD is a quadrilateral whose vertices are A(2, 2), B(2, –2), C(0, –1) and D(0, 1).
1) Reflect quadrilateral ABCD on the y-axis and name it as A'B'CD
2) Write down the coordinates of A' and B'.
3) Name two points which are invariant under the above reflection
4) Name the polygon A'B'CD
Three vertices of parallelogram ABCD taken in order are A(3, 6), B(5, 10) and C(3, 2)
1) the coordinate of the fourth vertex D
2) length of diagonal BD
3) equation of the side AD of the parallelogram ABCD
A straight line passes through the points P(–1, 4) and Q(5, –2). It intersects the co-ordinate axes at points A and B. M is the mid-point of the segment AB. Find:
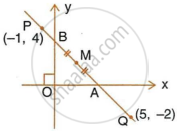
- The equation of the line.
- The co-ordinates of A and B.
- The co-ordinates of M.
A line through origin meets the line x = 3y + 2 at right angles at point X. Find the co-ordinates of X.
A line AB meets the x-axis at point A and y-axis at point B. The point P(−4, −2) divides the line segment AB internally such that AP : PB = 1 : 2. Find:
- the co-ordinates of A and B.
- equation of line through P and perpendicular to AB.
Point A and B have co-ordinates (7, −3) and (1, 9) respectively. Find:
- the slope of AB.
- the equation of perpendicular bisector of the line segment AB.
- the value of ‘p’ of (−2, p) lies on it.
Use a graph sheet for this question.
Take 1 cm = 1 unit along both x and y axis.
(i) Plot the following points:
A(0,5), B(3,0), C(1,0) and D(1,–5)
(ii) Reflect the points B, C and D on the y axis and name them as B',C'andD' respectively.
(iii) Write down the coordinates of B',C 'and D'
(iv) Join the point A, B, C, D, D ', C ', B', A in order and give a name to the closed figure ABCDD'C'B
A line is of length 10 units and one end is at the point (2, – 3). If the abscissa of the other end be 10, prove that its ordinate must be 3 or – 9.
