Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Using de Broglie’s hypothesis, explain with the help of a suitable diagram, Bohr’s second postulate of quantization of energy levels in a hydrogen atom.
उत्तर
De Broglie’s Explanation of Bohr’s Second Postulate of Quantisation
• De-Broglie’s hypothesis that electron has a wavelength λ = h/mv gave an explanation for Bohr’s quantised orbits by bringing in the wave particle duality.
• Orbits correspond to circular standing waves in which the circumference of the orbits equal whole number of wavelength.
According to de Broglie’s hypothesis
`lambda = h/p`also for Bohr’s model
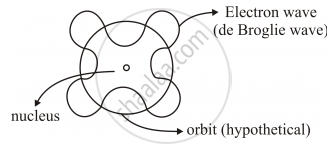
It states,
`nlambda = 2pir`
`=> n h/p = 2pir`
`=> rp =n h/(2pi) ` (as rp =L)
`=> L=n h/(2pi)` Bohr's 2ndPostulate
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A proton and an α -particle are accelerated through the same potential difference. Which one of the two has greater de-Broglie wavelength Justify your answer.
An α-particle and a proton are accelerated through the same potential difference. Find the ratio of their de Broglie wavelength.
A proton and an alpha particle are accelerated through the same potential. Which one of the two has (i) greater value of de−Broglie wavelength associated with it and (ii) less kinetic energy. Give reasons to justify your answer.
An electron is accelerated from rest through a potential V. Obtain the expression for the de-Broglie wavelength associated with it ?
A proton and an electron have same velocity. Which one has greater de-Broglie wavelength and why?
Find the de Broglie wavelength of electrons moving with a speed of 7 × 106 ms -1.
Describe in brief what is observed when moving electrons are allowed to fall on a thin graphite film and the emergent beam falls on a fluorescent screen.
Gas exerts pressure on the walls of the container because :
A litre of an ideal gas at 27°C is heated at constant pressure to 297°C. The approximate final volume of the gas is?
The kinetic energy of electron in (electron volt) moving with the velocity of 4 × 106 m/s will be
