Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What are hydrate isomers? Explain with an example.
उत्तर
The exchange of free solvent molecules such as water, ammonia, alcohol, etc., in the crystal lattice with a ligand in the coordination entity, will give different isomers. These types of isomers are called solvate isomers. If the solvent molecule is water, then these isomers are called hydrate isomers.
For example, the complex with the chemical formula \[\ce{CrCl3.+6H2O}\] has three hydrate isomers as shown below.
| \[\ce{[Cr(H2O)6]Cl3}\] | a violet colour compound and gives three chloride ions in solution |
| \[\ce{[Cr(H2O)5Cl]Cl2.H2O}\] | a pale green colour compound and gives two chloride ions in solution |
| \[\ce{[Cr(H2O)4Cl2]Cl.2H2O}\] | dark green colour compound and gives one chloride ion in solution |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Out of 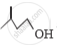 and
and 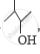 , which one is optically active and why ?
, which one is optically active and why ?
Choose the most correct option.
Which of the following complexes exist as cis and trans isomers?
1. [Cr(NH3)2Cl4]-
2. [Co(NH3)5Br]2⊕
3. [PtCl2Br2]2- (square planar)
4. [FeCl2(NCS)2]2- (tetrahedral)
Draw isomers of the following.
\[\ce{Pt(NH3)2ClNO2}\]
Which type of isomerism is exhibited by [Pt(NH3)2Cl2]?
Which one of the following complexes is not expected to exhibit isomerism?
Explain optical isomerism in coordination compounds with an example.
Which of the following is NOT a pair of structural isomers?
The relationship between compound (i) and (ii) is
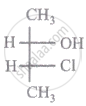 |
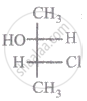 |
| (i) | (ii) |
The number of geometrical isomers of \[\ce{[Co(NH3)3 (NO3)3]}\] are ______.
Match the pairs in column I (pairs of isomers) and column II (types of isomers)
| Column I (Pairs of isomers) |
Column II (Types of isomers) |
| (A) [Cr(H2O)5Cl]Cl2.H2O and [Cr(H2O)4Cl2]Cl.2H2O | (i) Ionization isomers |
| (B) [Co(en)2(NO2)2]+ and [Co(en)2(ONO2)]+ | (ii) Hydrate isomers |
| (C) [Co(NH3)6] [Cr(CN)6] and [Cr(NH3)6] [Co(CN)6] | (iii) Linkage isomers |
| (D) [Pt(NH3)4Cl2] Br2 and [Pt(NH3)4Br2]Cl2 | (iv) Coordination isomers |
