Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain optical isomerism in coordination compounds with an example.
उत्तर
1. Coordination compounds which possess chirality exhibit optical isomerism similar to organic compounds.
2. The pair of two optically active isomers which are mirror images of each other are called enantiomers.
3. Their solutions rotate the plane of the plane polarised light either clockwise or anticlockwise and the corresponding isomers are called d (dextrorotatory) and 1 (levorotatory) forms respectively.
4. The octahedral complexes of type [M(xx)3]n±, [M(xx)2AB]n± and [M(xx)2B2]n± exhibit optical isomerism.
Examples:
1. The optical isomers of [Co(en)3]3+ are shown below.

Optical isomer
2. The coordination complex [COCl2(en)2]+ has three isomers, two optically active cis forms and one optically inactive transform. These structures are shown below.

Optical isomers
3. In a coordination compound of type [PtCl2(en)2]2+, two geometrical isomers are possible. They are cis and trans. Among these two isomers, cis isomer shows optically active isomerism because the whole molecule is asymmetric.
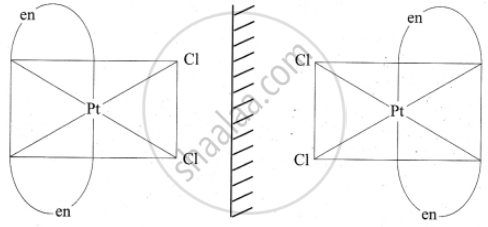
Optical isomers of Cis [PtCl2(en)2]2+
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw optical isomers of [Co(en)3]3+.
What is linkage isomerism? Explain with an example.
Geometrical isomerism is not shown by
Which of the following shows maximum number of isomers?
Draw geometric isomers of the following complex.
Geometrical isomers of Pt(NH3)2Cl2
Give cis isomer of [Co(NH3)4Cl2]⊕.
Give trans isomer of [Co(NH3)4Cl2]⊕.
Explain the geometrical isomerism of the octahedral complex of the type [M(AA)2B2]n± with a suitable example.
Explain the ionisation isomers.
Which one of the following complex ions has geometrical isomers?
