Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What change will you observe if intensity of incident radiation is changed but the frequency remains the same?
उत्तर
If intensity of incident radiation is changed but the frequency remains the same, the plot will be
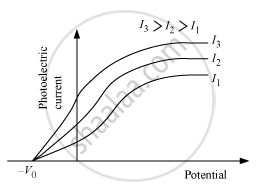
If the intensity of incident radiation is changed but the frequency remains the same in this case the stopping potential remains unchanged.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The photoelectric work function for a metal surface is 2.3 eV. If the light of wavelength 6800A is incident on the surface of metal, find threshold frequency and incident frequency. Will there be an emission of photoelectrons or not?
[Velocity of light c = 3 x 108 m/s,
Planck’s constant, h = 6.63 * 10-34 Js ]
Sketch the graphs showing variation of stopping potential with frequency of incident radiations for two photosensitive materials A and B having threshold frequencies vA > vB.
(i) In which case is the stopping potential more and why?
(ii) Does the slope of the graph depend on the nature of the material used? Explain.
The photoelectric work function for a metal is 4.2 eV. If the stopping potential is 3V, find the threshold wavelength and maximum kinetic energy of emitted electrons.
(Velocity of light in air = 3 x 108m/s,
Planck's constant = 6·63 x10-34 J -s,
Charg.e ori electron = 1·6 x 10 -19 C)
Two monochromatic beams, one red and the other blue, have the same intensity. In which case (i) the number of photons per unit area per second is larger, (ii) the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons is more? Justify your answer.
Draw a plot showing the variation of photoelectric current versus the intensity of incident radiation on a given photosensitive surface.
A photosensitive surface emits photoelectrons when red light falls on it. Will the surface emit photoelectrons when blue light is incident on it? Give reason.
Draw a plot showing the variation of photoelectric current with collector potential for different frequencies but same intensity of incident radiation ?
With reference to the photoelectric effect, what is meant by threshold wavelength?
Two metals A and B have work functions 4 eV and 6 eV respectively. Which metal has a lower threshold wavelength for photoelectric effect?
State how will you use this graph to detennine the value of Planck's constant.
