Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
When a particle moves in a circle with a uniform speed
विकल्प
its velocity and acceleration are both constant
its velocity is constant but the acceleration changes
its acceleration is constant but the velocity changes
its velocity and acceleration both change.
उत्तर
its velocity and acceleration both change.
In a circular motion, the direction of particle changes. Therefore, velocity, being a vector quantity, also changes.
As the velocity changes, acceleration also changes.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A 70 kg man stands in contact against the inner wall of a hollow cylindrical drum of radius 3 m rotating about its vertical axis with 200 rev/min. The coefficient of friction between the wall and his clothing is 0.15. What is the minimum rotational speed of the cylinder to enable the man to remain stuck to the wall (without falling) when the floor is suddenly removed?
Tow cars having masses m1 and m2 moves in circles of radii r1 and r2 respectively. If they complete the circle in equal time, the ratio of their angular speed ω1/ω2 is
A motorcycle is going on an overbridge of radius R. The driver maintains a constant speed. As the motorcycle is ascending on the overbridge, the normal force on it
A simple pendulum having a bob of mass m is suspended from the ceiling of a car used in a stunt film shooting. the car moves up along an inclined cliff at a speed v and makes a jump to leave the cliff and lands at some distance. Let R be the maximum height of the car from the top of the cliff. The tension in the string when the car is in air is
An object follows a curved path. The following quantities may remain constant during the motion
(a) speed
(b) velocity
(c) acceleration
(d) magnitude of acceleration.
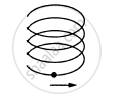
A particle is going in a spiral path as shown in figure with constant speed.
A ceiling fan has a diameter (of the circle through the outer edges of the three blades) of 120 cm and rpm 1500 at full speed. Consider a particle of mass 1 g sticking at the outer end of a blade. How much force does it experience when the fan runs at full speed? Who exerts this force on the particle? How much force does the particle exert on the blade along its surface?
Suppose the amplitude of a simple pendulum having a bob of mass m is θ0. Find the tension in the string when the bob is at its extreme position.
A motorcycle has to move with a constant speed on an over bridge which is in the form of a circular arc of radius R and has a total length L. Suppose the motorcycle starts from the highest point.(a) What can its maximum velocity be for which the contact with the road is not broken at the highest point? (b) If the motorcycle goes at speed 1/√2 times the maximum found in part (a), where will it lose the contact with the road? (c) What maximum uniform speed can it maintain on the bridge if it does not lose contact anywhere on the bridge?
A block of mass m moves on a horizontal circle against the wall of a cylindrical room of radius R. The floor of the room on which the block moves is smooth but the friction coefficient between the wall and the block is μ. The block is given an initial speed v0. As a function of the speed v writes
(a) the normal force by the wall on the block,
(b) the frictional force by a wall, and
(c) the tangential acceleration of the block.
(d) Integrate the tangential acceleration \[\left( \frac{dv}{dt} = v\frac{dv}{ds} \right)\] to obtain the speed of the block after one revolution.
When seen from below, the blades of a ceiling fan are seen to be revolving anticlockwise and their speed is decreasing. Select the correct statement about the directions of its angular velocity and angular acceleration.
Two particles A and B are located at distances rA and rB respectively from the centre of a rotating disc such that rA > rB. In this case, if angular velocity ω of rotation is constant, then ______
A rope is wound around a solid cylinder of mass 1 kg and radius 0.4 m. What is the angular acceleration of cylinder, if the rope is pulled with a force of 25 N? (Cylinder is rotating about its own axis.)
A rigid body is rotating with angular velocity 'ω' about an axis of rotation. Let 'v' be the linear velocity of particle which is at perpendicular distance 'r' from the axis of rotation. Then the relation 'v = rω' implies that ______.
If a cyclist doubles his speed while negotiating a curve, how does the tendency to overturn vary?
A body of mass m is performing a UCM in a circle of radius r with speed v. The work done by the centripetal force in moving it through `(2/3)`rd of the circular path is ______.
In negotiating curve on a flat road, a cyclist leans inwards by an angle e with the vertical in order to ______.
A body is moving along a circular track of radius 100 m with velocity 20 m/s. Its tangential acceleration is 3 m/s2 then its resultant accelaration will be ______.
A racing car travels on a track (without banking) ABCDEFA (Figure). ABC is a circular arc of radius 2 R. CD and FA are straight paths of length R and DEF is a circular arc of radius R = 100 m. The co-efficient of friction on the road is µ = 0.1. The maximum speed of the car is 50 ms–1. Find the minimum time for completing one round.

Find the angular acceleration of a particle in circular motion which slows down from 300 r.p.m. to 0 r.p.m. in 20 s.
