Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
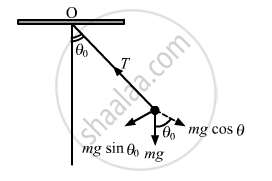
Suppose the amplitude of a simple pendulum having a bob of mass m is θ0. Find the tension in the string when the bob is at its extreme position.
उत्तर
Let T be the tension in the string at the extreme position.
Velocity of the pendulum is zero at the extreme position.
So, there is no centripetal force on the bob.
∴ T = mgcosθ0
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A thin circular loop of radius R rotates about its vertical diameter with an angular frequency ω. Show that a small bead on the wire loop remains at its lowermost point for `omega <= sqrt(g/R)` .What is the angle made by the radius vector joining the centre to the bead with the vertical downward direction for `omega = sqrt("2g"/R)` ?Neglect friction.
When a particle moves in a circle with a uniform speed
A stone of mass m tied to a string of length l is rotated in a circle with the other end of the string as the centre. The speed of the stone is v. If the string breaks, the stone will move
If the earth stop rotating, the apparent value of g on its surface will
A ceiling fan has a diameter (of the circle through the outer edges of the three blades) of 120 cm and rpm 1500 at full speed. Consider a particle of mass 1 g sticking at the outer end of a blade. How much force does it experience when the fan runs at full speed? Who exerts this force on the particle? How much force does the particle exert on the blade along its surface?
A simple pendulum is suspended from the ceiling of a car taking a turn of radius 10 m at a speed of 36 km/h. Find the angle made by he string of the pendulum with the vertical if this angle does not change during the turn. Take g = 10 m/s2.
A turn of radius 20 m is banked for the vehicles going at a speed of 36 km/h. If the coefficient of static friction between the road and the tyre is 0.4, what are the possible speeds of a vehicle so that it neither slips down nor skids up?
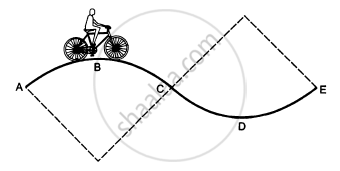
A track consists of two circular parts ABC and CDE of equal radius 100 m and joined smoothly as shown in figure. Each part subtends a right angle at its centre. A cycle weighing 100 kg together with the rider travels at a constant speed of 18 km/h on the track. (a) Find the normal contact force by the road on the cycle when it is at B and at D. (b) Find the force of friction exerted by the track on the tyres when the cycle is at B, C and. (c) Find the normal force between the road and the cycle just before and just after the cycle crosses C. (d) What should be the minimum friction coefficient between the road and the tyre, which will ensure that the cyclist can move with constant speed? Take g = 10 m/s2.
What is the radius of curvature of the parabola traced out by the projectile in the previous problem at a point where the particle velocity makes an angle θ/2 with the horizontal?
Choose the correct option.
Select correct statement about the formula (expression) of moment of inertia (M.I.) in terms of mass M of the object and some of its distance parameter/s, such as R, L, etc.
In a certain unit, the radius of gyration of a uniform disc about its central and transverse axis is `sqrt2.5`. Its radius of gyration about a tangent in its plane (in the same unit) must be ______.
In non-uniform circular motion, the ratio of tangential to radial acceleration is (r = radius, a = angular acceleration and v = linear velocity)
A body slides down a smooth inclined plane having angle θ and reaches the bottom with velocity v. If a body is a sphere, then its linear velocity at the bottom of the plane is
A particle of mass m is performing UCM along a circle of radius r. The relation between centripetal acceleration a and kinetic energy E is given by
A body of mass m is performing a UCM in a circle of radius r with speed v. The work done by the centripetal force in moving it through `(2/3)`rd of the circular path is ______.
In negotiating curve on a flat road, a cyclist leans inwards by an angle e with the vertical in order to ______.
When a body slides down from rest along a smooth inclined plane making an angle of 45° with the horizontal, it takes time T. When the same body slides down from rest along a rough inclined plane making the same angle and through the same distance, it is seen to take time pT, where p is some number greater than 1. Calculate the co-efficient of friction between the body and the rough plane.
