Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Choose the correct option.
Select correct statement about the formula (expression) of moment of inertia (M.I.) in terms of mass M of the object and some of its distance parameter/s, such as R, L, etc.
विकल्प
Different objects must have different expressions for their M.I.
When rotating about their central axis, a hollow right circular cone and a disc have the same expression for the M.I.
Expression for the M.I. for a parallelepiped rotating about the transverse axis passing through its centre includes its depth.
Expression for M.I. of a rod and that of a plane sheet is the same about a transverse axis.
उत्तर
When rotating about their central axis, a hollow right circular cone and a disc have the same expression for the M.I.
Explanation:
Expression for M.I of a hollow right circular cone is given by:
Here, m and R are mass and radius of gyration respectively.
And expression for M.I of disc is given by:
Here, m and R are mass and radius of gyration, respectively.
Thus, when rotating about their central axis, a hollow right circular cone and a disc have the same expression for the M.I.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
You may have seen in a circus a motorcyclist driving in vertical loops inside a ‘death-well’ (a hollow spherical chamber with holes, so the spectators can watch from outside). Explain clearly why the motorcyclist does not drop down when he is at the uppermost point, with no support from below. What is the minimum speed required at the uppermost position to perform a vertical loop if the radius of the chamber is 25 m?
A 70 kg man stands in contact against the inner wall of a hollow cylindrical drum of radius 3 m rotating about its vertical axis with 200 rev/min. The coefficient of friction between the wall and his clothing is 0.15. What is the minimum rotational speed of the cylinder to enable the man to remain stuck to the wall (without falling) when the floor is suddenly removed?
A thin circular loop of radius R rotates about its vertical diameter with an angular frequency ω. Show that a small bead on the wire loop remains at its lowermost point for `omega <= sqrt(g/R)` .What is the angle made by the radius vector joining the centre to the bead with the vertical downward direction for `omega = sqrt("2g"/R)` ?Neglect friction.
Tow cars having masses m1 and m2 moves in circles of radii r1 and r2 respectively. If they complete the circle in equal time, the ratio of their angular speed ω1/ω2 is
Water in a bucket is whirled in a vertical circle with string attached to it. The water does no fall down even when the bucket is inverted at the top of its path. We conclude that in this position
A motorcycle is going on an overbridge of radius R. The driver maintains a constant speed. As the motorcycle is ascending on the overbridge, the normal force on it
A train A runs from east to west and another train B of the same mass runs from west to east at the same speed along the equator. A presses the track with a force F1 and B presses the track with a force F2.
A rod of length L is pivoted at one end and is rotated with a uniform angular velocity in a horizontal plane. Let T1 and T2 be the tensions at the points L/4 and 3L/4 away from the pivoted ends.
Find the acceleration of the moon with respect to the earth from the following data:
Distance between the earth and the moon = 3.85 × 105 km and the time taken by the moon to complete one revolution around the earth = 27.3 days.
A scooter weighing 150 kg together with its rider moving at 36 km/hr is to take a turn of a radius 30 m. What horizontal force on the scooter is needed to make the turn possible ?
A ceiling fan has a diameter (of the circle through the outer edges of the three blades) of 120 cm and rpm 1500 at full speed. Consider a particle of mass 1 g sticking at the outer end of a blade. How much force does it experience when the fan runs at full speed? Who exerts this force on the particle? How much force does the particle exert on the blade along its surface?
A simple pendulum is suspended from the ceiling of a car taking a turn of radius 10 m at a speed of 36 km/h. Find the angle made by he string of the pendulum with the vertical if this angle does not change during the turn. Take g = 10 m/s2.
A turn of radius 20 m is banked for the vehicles going at a speed of 36 km/h. If the coefficient of static friction between the road and the tyre is 0.4, what are the possible speeds of a vehicle so that it neither slips down nor skids up?
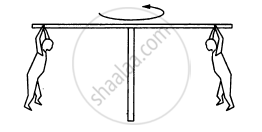
In a children's park a heavy rod is pivoted at the centre and is made to rotate about the pivot so that the rod always remains horizontal. Two kids hold the rod near the ends and thus rotate with the rod (In the following figure). Let the mass of each kid be 15 kg, the distance between the points of the rod where the two kids hold it be 3.0 m and suppose that the rod rotates at the rate of 20 revolutions per minute. Find the force of friction exerted by the rod on one of the kids.
What is the radius of curvature of the parabola traced out by the projectile in the previous problem at a point where the particle velocity makes an angle θ/2 with the horizontal?
A block of mass m moves on a horizontal circle against the wall of a cylindrical room of radius R. The floor of the room on which the block moves is smooth but the friction coefficient between the wall and the block is μ. The block is given an initial speed v0. As a function of the speed v writes
(a) the normal force by the wall on the block,
(b) the frictional force by a wall, and
(c) the tangential acceleration of the block.
(d) Integrate the tangential acceleration \[\left( \frac{dv}{dt} = v\frac{dv}{ds} \right)\] to obtain the speed of the block after one revolution.
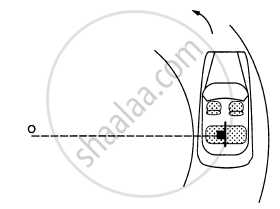
A car moving at a speed of 36 km/hr is taking a turn on a circular road of radius 50 m. A small wooden plate is kept on the seat with its plane perpendicular to the radius of the circular road (In the following figure). A small block of mass 100 g is kept on the seat which rests against the plate. the friction coefficient between the block and the plate is. (a) Find the normal contact force exerted by the plate on the block. (b) The plate is slowly turned so that the angle between the normal to the plate and the radius of the road slowly increases. Find the angle at which the block will just start sliding on the plate.
Choose the correct option.
Consider the following cases:
(P) A planet revolving in an elliptical orbit.
(Q) A planet revolving in a circular orbit.
Principle of conservation of angular momentum comes in force in which of these?
A body slides down a smooth inclined plane having angle θ and reaches the bottom with velocity v. If a body is a sphere, then its linear velocity at the bottom of the plane is
The escape velocity of a body from any planet, whose mass is six times the mass of earth and radius is twice the radius of earth will be
(v8 = escape velocity of a body from the earth's surface).
A person driving a car suddenly applies the brakes on seeing a child on the road ahead. If he is not wearing seat belt, he falls forward and hits his head against the steering wheel. Why?
When a body slides down from rest along a smooth inclined plane making an angle of 45° with the horizontal, it takes time T. When the same body slides down from rest along a rough inclined plane making the same angle and through the same distance, it is seen to take time pT, where p is some number greater than 1. Calculate the co-efficient of friction between the body and the rough plane.
A racing car travels on a track (without banking) ABCDEFA (Figure). ABC is a circular arc of radius 2 R. CD and FA are straight paths of length R and DEF is a circular arc of radius R = 100 m. The co-efficient of friction on the road is µ = 0.1. The maximum speed of the car is 50 ms–1. Find the minimum time for completing one round.

A block of 200 g mass moves with a uniform speed in a horizontal circular groove, with vertical side walls of radius 20 cm. If the block takes 40 s to complete one round, the normal force by the side walls of the groove is ______.
Find the angular acceleration of a particle in circular motion which slows down from 300 r.p.m. to 0 r.p.m. in 20 s.
