Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Which of the following quantities remain constant in a planetary motion (consider elliptical orbits) as seen from the sun?
विकल्प
Speed
Angular speed
Kinetic Energy
Angular momentum.
उत्तर
Angular momentum.
In planetary motion, the net external torque on the planet is zero. Therefore, angular momentum will remain constant.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write the answer of the question with reference to laws of gravitation.
State the universal law of gravitation.
What happens to the force between two objects, if the mass of one object is doubled?
Calculate the force of gravitation between the earth and the Sun, given that the mass of the earth = 6 × 1024 kg and of the Sun = 2 × 1030 kg. The average distance between the two is 1.5 × 1011 m.
Choose the correct alternative:
Acceleration due to gravity increases/decreases with increasing altitude.
Which of the Kepler’s laws of planetary motion led Newton to establish the inverse-square rule for gravitational force between two bodies ?
Can we apply Newton’s third law to the gravitational force ? Explain your answer.
State the universal law of gravitation. Name the scientist who gave this law.
State and explain Kepler's laws of planetary motion. Draw diagrams to illustrate these laws.
The weight of an object is more at the poles than at the equator. Is it beneficial to purchase goods at equator and sell them at the pole? Does it matter whether a spring balance is used or an equal-beam balance is used?
Let V and E be the gravitational potential and gravitational field at a distance r from the centre of a uniform spherical shell. Consider the following two statements :
(A) The plot of V against r is discontinuous.
(B) The plot of E against r is discontinuous.
A body is suspended from a spring balance kept in a satellite. The reading of the balance is W1 when the satellite goes in an orbit of radius R and is W2 when it goes in an orbit of radius 2 −R.
Consider a planet moving in an elliptical orbit round the sun. The work done on the planet by the gravitational force of the sun
(a) is zero in any small part of the orbit
(b) is zero in some parts of the orbit
(c) is zero in one complete revolution
(d) is zero in no part of the motion.
A tunnel is dug along a diameter of the earth. Find the force on a particle of mass m placed in the tunnel at a distance x from the centre.
A ball is thrown vertically upwards. It goes to a height 20 m and then returns to the ground. Taking acceleration due to gravity g to be 10 ms-2, find: the initial velocity of the ball.
How will the force of gravitation between two objects change if the distance between them is:
Infinite
Where will you weigh more: at the moon's surface or at the earth's surface?
What is meant by the equation :
`g= Gxxm/r^2`
where the symbols have their usual meanings.
At what height above the earth's surface would the value of acceleration due to gravity be half of what it is on the surface? Take the radius of earth to be R.
State Newton's universal law of gravitation. Express it with the mathematical form of force of gravitation?
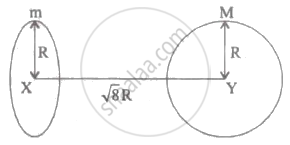
Find the gravitational force of attraction between the ring and sphere as shown in the diagram, where the plane of the ring is perpendicular to the line joining the centres. If `sqrt8` R is the distance between the centres of a ring (of mass 'm')and a sphere (mass 'M') where both have equal radius 'R'.