Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A tunnel is dug along a diameter of the earth. Find the force on a particle of mass m placed in the tunnel at a distance x from the centre.
उत्तर
Mass of the Earth,
\[M = \left( \frac{4}{3} \right)\pi R^3 \rho\] ...(i)
Consider an imaginary sphere of radius x with centre O as shown in the figure below :
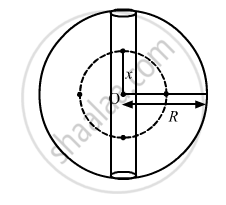
\[\text { Mass of the imaginary sphere }, M' = \left( \frac{4}{3} \right)\pi x^3 \rho . . . (ii)\]
\[\text { From (i) and (ii), we have : }\]
\[\frac{M'}{M} = \frac{x^3}{R^3}\]
∴ Gravitational force on the particle of mass m is given by F \[= \frac{GMm}{x^2}\]
\[\Rightarrow F = \frac{GM x^3 m}{R^3 x^2} = \frac{GMm}{R^3}x\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What happens to the force between two objects, if the mass of one object is doubled?
What happens to the force between two objects, if the distance between the objects is doubled and tripled?
Write the three laws given by Kepler. How did they help Newton to arrive at the inverse square law of gravity?
At noon, the sun and the earth pull the objects on the earth's surface in opposite directions. At midnight, the sun and the earth pull these objects in same direction. Is the weight of an object, as measured by a spring balance on the earth's surface, more at midnight as compared to its weight at noon?
Suppose the gravitational potential due to a small system is k/r2 at a distance r from it. What will be the gravitational field? Can you think of any such system? What happens if there were negative masses?
Consider a planet moving in an elliptical orbit round the sun. The work done on the planet by the gravitational force of the sun
(a) is zero in any small part of the orbit
(b) is zero in some parts of the orbit
(c) is zero in one complete revolution
(d) is zero in no part of the motion.
A semicircular wire has a length L and mass M. A particle of mass m is placed at the centre of the circle. Find the gravitational attraction on the particle due to the wire.
The law of gravitation gives the gravitational force between :
Where will you weigh more: at the centre of the earth or at the surface of the earth?
Where will you weigh more: at the moon's surface or at the earth's surface?
Explain why:
The atmosphere does not escape.
What do you mean by a gravitational constant?
Solve the following problem.
Find the gravitational force between the Sun and the Earth.
Given Mass of the Sun = 1.99 × 1030 kg
Mass of the Earth = 5.98 × 1024 kg
The average distance between the Earth and the Sun = 1.5 × 1011 m.
Solve the following problem.
Calculate the acceleration due to gravity at a height of 300 km from the surface of the Earth. (M = 5.98 × 1024 kg, R = 6400 km).
Mahendra and Virat are sitting at a distance of 1 m from each other.Their masses are 75 kg and 80 kg respectively. What is the gravitational force between them? (G = 6.67 × 10-11 Nm2/kg2)
State Newton's universal law of gravitation. Express it with the mathematical form of force of gravitation?
Give scientific reasons for the following:
Newton's gravitational law is the universal law of gravitation.
