Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A tunnel is dug along a chord of the earth at a perpendicular distance R/2 from the earth's centre. The wall of the tunnel may be assumed to be frictionless. Find the force exerted by the wall on a particle of mass m when it is at a distance x from the centre of the tunnel.
उत्तर
Let d be distance of the particle from the centre of the Earth.
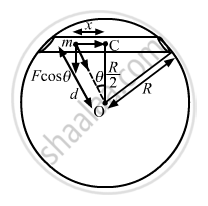
\[\text { Now }, d^2 = x^2 + \left( \frac{R^2}{4} \right) = \frac{4 x^2 + R^2}{4}\]
\[ \Rightarrow d = \left( \frac{1}{2} \right)\sqrt{4 x^2 + R^2}\]
Let M be the mass of the Earth and M' be the mass of the sphere of radius d.
Then we have :
\[M = \left( \frac{4}{3} \right)\pi R^3 \rho\]
\[ M^1 = \left( \frac{4}{3} \right)\pi d^3 \rho\]
\[ \therefore \frac{M^1}{M} = \frac{d^3}{R^3}\]
Gravitational force on the particle of mass m is given by
\[F = \frac{G M^1 m}{d^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow F = \frac{G d^3 Mm}{R^3 d^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow F = \frac{GMm}{R^3}d\]
∴ Normal force exerted by the wall, FN = F cos θ
\[= \frac{GMmd}{R^3} \times \frac{R}{2d} = \frac{GMm}{2 R^2}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What happens to the force between two objects, if the distance between the objects is doubled and tripled?
Can we apply Newton’s third law to the gravitational force ? Explain your answer.
At noon, the sun and the earth pull the objects on the earth's surface in opposite directions. At midnight, the sun and the earth pull these objects in same direction. Is the weight of an object, as measured by a spring balance on the earth's surface, more at midnight as compared to its weight at noon?
Which of the following quantities remain constant in a planetary motion (consider elliptical orbits) as seen from the sun?
Two spherical balls of mass 10 kg each are placed 10 cm apart. Find the gravitational force of attraction between them.
The mass of moon is about 0.012 times that of earth and its diameter is about 0.25 times that of earth. The value of G on the moon will be:
Write an expression for the gravitational force of attraction between two bodies of masses m1 and m2 separated by a distance r.
How will the force of gravitation between two objects change if the distance between them is:
Halved
How will the force of gravitation between two objects change if the distance between them is:
Infinite
How will the force of gravitation between two objects change if the distance between them is:
Almost zero
A ball is thrown up with a speed of 4.9 ms-1.
Prove that the time of ascent is equal to the time of descent.
You can change the direction in which an object is moving by___________.
What is the difference between gravity and gravitation?
Gravity is another kind of ________. It exerts all through the ________. The Sun's gravity keeps the ___________ in their orbits. Gravity can only be felt with very large ________.
Explain the difference between g and G.
Solve the following problem.
Calculate the acceleration due to gravity at a height of 300 km from the surface of the Earth. (M = 5.98 × 1024 kg, R = 6400 km).
To project the rockets which of the following principle(s) is /(are) required?
Complete the chart below.
| F(N) | M1(kg) | M2(kg) | D(m) |
| (a) | 50 | 84 | 02 |
| 16 × 109 | 1.63 × 1022 | (b) | 34 |
Answer the following questions in reference to the figure below:
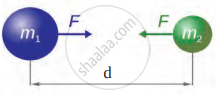
- Which relation is shown in the figure?
- What will happen if the mass of one of the objects is doubled?
