Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Which of the following (referred to a spherical mirror) do (does) not depend on whether the rays are paraxial or not?
(a) Pole
(b) Focus
(c) Radius of curvature
(d) Principal axis
उत्तर
(a) Pole
(c) Radius of curvature
(d) Principal axis
Paraxial rays are the light rays close to the principal axis. The focus of the spherical mirror for paraxial rays are different from the focus for marginal rays. So, the focus depends on whether the rays are paraxial or marginal. The pole, radius of curvature and the principal axis of a spherical mirror do not depend on paraxial or marginal rays.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Use the mirror equation to show that an object placed between f and 2f of a concave mirror produces a real image beyond 2f.
Use the mirror equation to show that a convex mirror always produces a virtual image independent of the location of the object.
Use the mirror equation to deduce that an object placed between the pole and focus of a concave mirror produces a virtual and enlarged image.
An object is kept on the principal axis of a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm. at a distance of 15
cm from its pole. The image formed by the mirror is:
(a) Virtual and magnified
(b) Virtual and diminished
(c) Real and magnified
(d) Real and diminished
Use the mirror equation to show that an object placed between f and 2f of a concave mirror forms an image beyond 2f.
Define the term 'limit of resolution'?
Use the mirror equation to show a convex mirror always produces a virtual image independent of the location of the object ?
Can a plane mirror ever form a real image?
A point source of light is placed in front of a plane mirror.
The rays of different colours fail to converge at a point after going through a converging lens. This defect is called
Mark the correct options.
A light ray falling at an angle of 45° with the surface of a clean slab of ice of thickness 1.00 m is refracted into it at an angle of 30°. Calculate the time taken by the light rays to cross the slab. Speed of light in vacuum = 3 × 108 m s−1.
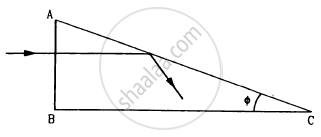
A light ray is incident normally on the face AB of a right-angled prism ABC (μ = 1.50) as shown in figure. What is the largest angle ϕ for which the light ray is totally reflected at the surface AC?
Find the maximum angle of refraction when a light ray is refracted from glass (μ = 1.50) to air.
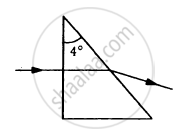
Find the angle of deviation suffered by the light ray shown in figure. The refractive index μ = 1.5 for the prism material.
A light ray, going through a prism with the angle of prism 60°, is found to deviate by 30°. What limit on the refractive index can be put from these data?
The focal length f is related to the radius of curvature r of the spherical convex mirror by ______.
An upright object is placed at a distance of 40 cm in front of a convergent lens of a focal length of 20 cm. A convergent mirror of focal length 10 cm is placed at a distance of 60 cm on the other side of the lens. The position and size of the final image will be ______.
