Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Which of the following carbocation is most stable?
विकल्प
\[\ce{(CH3)3C*^+CH2}\]
\[\ce{(CH3)3^+C}\]
\[\ce{CH3CH2^+CH2}\]
\[\ce{CH3^+CH CH2C}\]
उत्तर
\[\ce{(CH3)3^+C}\]
Explanation:
\[\ce{(CH3)3^+C}\] is a tertiary carbocation. A tertiary carbocation is the most stable carbocation due to the electron releasing effect of three methyl groups. An increased + I effect by three methyl groups stabilizes the positive charge on the carbocation.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
For the following bond cleavages, use curved arrows to show the electron flow and classify homolysis or heterolysis. Identify reactive intermediate produced as free radical, carbocation and carbanion.
\[\ce{CH3O - OCH3 -> CH3\overset\bullet{\text{O}} + \overset\bullet{\text{O}}CH3}\]
For the following bond cleavages, use curved-arrows to show the electron flow and classify as homolysis or heterolysis. Identify reactive intermediate produced as free radical, carbocation and carbanion.
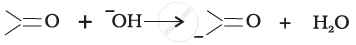
For the following bond cleavages, use curved-arrows to show the electron flow and classify as homolysis or heterolysis. Identify reactive intermediate produced as free radical, carbocation and carbanion.
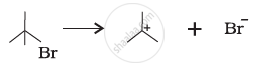
For the following bond cleavages, use curved-arrows to show the electron flow and classify as homolysis or heterolysis. Identify reactive intermediate produced as free radical, carbocation and carbanion.
What is the correct order of decreasing stability of the following cations.
| I. | \[\ce{CH3 - \overset{⊕}{C}H - CH3}\] |
| II. | \[\ce{CH3 - \overset{⊕}{C}H - OCH3}\] |
| III. | \[\ce{CH3 - \overset{⊕}{C}H - CH2 - OCH3}\] |
Covalent bond can undergo fission in two different ways. The correct representation involving a heterolytic fission of CH3 – Br is:
Write structures of various carbocations that can be obtained from 2-methylbutane. Arrange these carbocations in order of increasing stability.
Match the intermediates given in Column I with their probable structure in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Free radical | (a) Trigonal planar |
| (ii) Carbocation | (b) Pyramidal |
| (iii) Carbanion | (c) Linear |
Which of the following carbocation's is most stable?
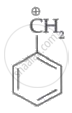 |
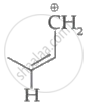 |
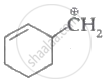 |
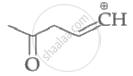 |
| (I) | (II) | (III) | (IV) |
Among the given species the resonance stabilised carbocations are:
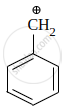 |
\[\ce{CH2 = \overset{⊕}{C}H}\] | \[\ce{CH3 - \overset{⊕}{C}H2}\] | \[\ce{HC ≡ \overset{⊕}{C}}\] |
| A | B | C | D |
The correct order of stability of given carbocation is:
A solution of (–) – 1 – chloro–1–phenylethane in toluene racemises slowly in the presence of a small amount of SbCl5, due to the formation of ______.
The increasing order of stability of the following free radicals is ______.
