Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Which of the following is an amorphous solid?
विकल्प
Graphite (C)
Quartz glass (SiO2)
Chrome alum
Silicon carbide (SiC)
उत्तर
Quartz glass (SiO2)
Explanation:
| Crystalline Silica (Quartz) | Amorphous Silica (Glass) | |
| 1. | Crystalline in nature. Also called quartz. | Light white powder. |
| 2. | All four corners of \[\ce{SiO4}\] tetrahedron are shared by others to give a network solid. | The \[\ce{sio4}\] tetrahedron are randomly joined giving rise to polymeric chains, sheets or three- dimensional units |
| 3. | High and sharp melting point (1710°C) | Does not have sharp melting point. On heating softens gradually to liquid. |
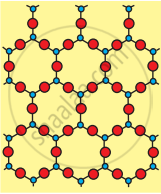
(a) Crystalline (Quartz)
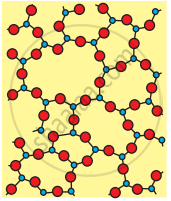
(b) Amorphous (Quartz glass)
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is the hybridisation of carbon atom in diamond and graphite?
Why are solids rigid?
Why do solids have a definite volume?
'Stability of a crystal is reflected in the magnitude of its melting point'. Comment. Collect melting points of solid water, ethyl alcohol, diethyl ether and methane from a data book. What can you say about the intermolecular forces between these molecules?
Most crystals show good cleavage because their atoms, ions or molecules are ____________.
“Crystalline solids are anisotropic in nature″. What is the meaning of anisotropic in the given statement?
Which of the following statement is not true about amorphous solids?
Which one of the following is non-crystalline or amorphous?
Under which situations can an amorphous substance change to crystalline form?
An ionic solid AB2 isomorphous to the rutile structure (a tetragonal system with the effective number of formula units = 2) has edge lengths of the unit cell of 4Å, 4Å and 7Å. The density of the substance is ______ mg/cc. (if its formula weight is 80. The NA = 6 × 1023 and express your answer in mg/cc using four significant digits.)
